Key Changes in Foreign Trade Policy 2023
- Blog|GST & Customs|
- 10 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 1 May, 2023

Table of Contents
- Export Growth Potential of India
- Foreign Trade Policy 2023
- Penal Provisions
- Export Promotion Schemes – Overview
- Advance Authorisation
- Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme (‘EPCG’)
- Relevant changes under AA and EPCG under FTP 2023
- Duty Drawback
- Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Products (RoDTEP)
- Taxes/duties remitted under RoDTEP
- Points to be noted
- EOU/STP Scheme – Overview and Features
- EOU/STP Scheme – Taxes on supply chain
- Status Holder (‘SH’) Scheme
- Clubbing of various schemes
- Deemed Export
- Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET)
- SCOMET
- Amnesty Scheme
1. Export Growth Potential of India
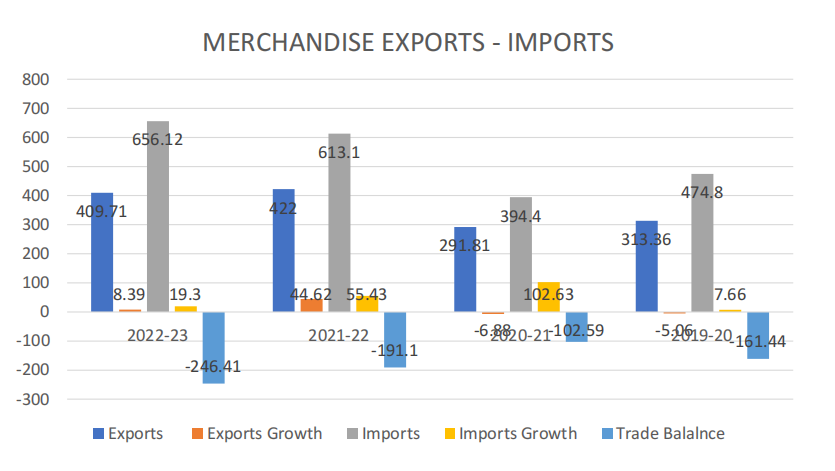
- Widening trade deficit, a cause of concern
- Service Exports USD 340.29 bn during 2022-23 (estimated) and USD 254 bn during 2021-22
- Free Trade Agreements with the UK, EU, Canada and other countries in advanced stages
- Foreign law firms allowed to operate in India
- Foreign Universities being allowed
- Focus on Make in India
2. Foreign Trade Policy 2023
1. Issued under Section 5 of the Foreign Trade (Development and Regulations) Act, 1992
2. Formulated and administered by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade
3. Consists of:
- FTP
- Handbook of Procedures
- Standard Input Output Norms (SION)
4. No end date to current FTP unlike previous FTPs which were valid for 5 years
5. Major policy shift from incentives on exports (like MEIS, SEIS etc) to remission of duties
6. Three new chapters introduced – Developing Districts as Export Hub (Chapter 3), Promoting Cross Border Trade in Digital Economy (Chapter 9) and SCOMET (Chapter 10)
7. Regulates import and export of goods from India
8. Goods are categorized in 3 category:
- Free: Import or export allowed without any licence or permission
- Restricted: Import allowed with licence/authorisations
- Prohibited: Import or export not allowed
9. Approvals or licences under other laws need to be obtained separately
10. To boost merchanting activities from India – Merchanting trade involving shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary allowed subject to compliance with RBI guidelines, except for goods/items in the CITES and SCOMET list
11. IEC mandatory for service exporters on the date of rendering service for availing benefits under FTP
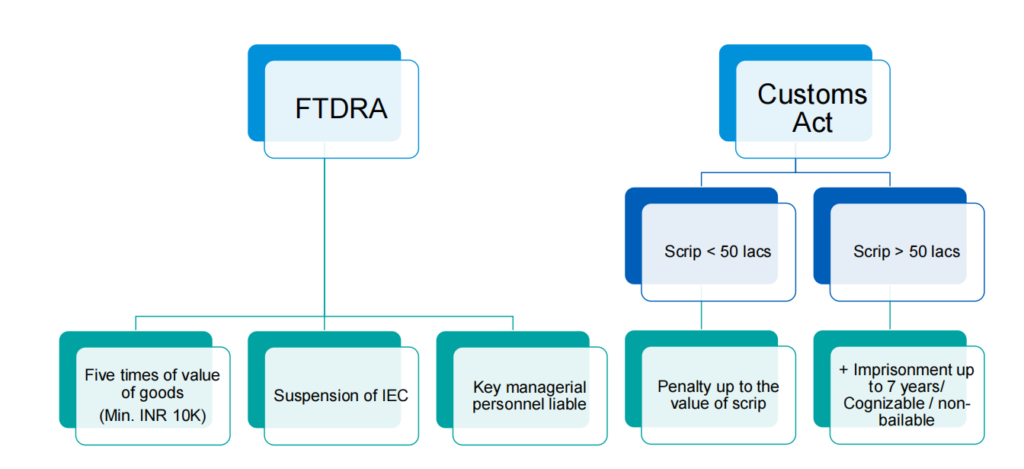
3. Penal Provisions
4. Export Promotion Schemes – Overview
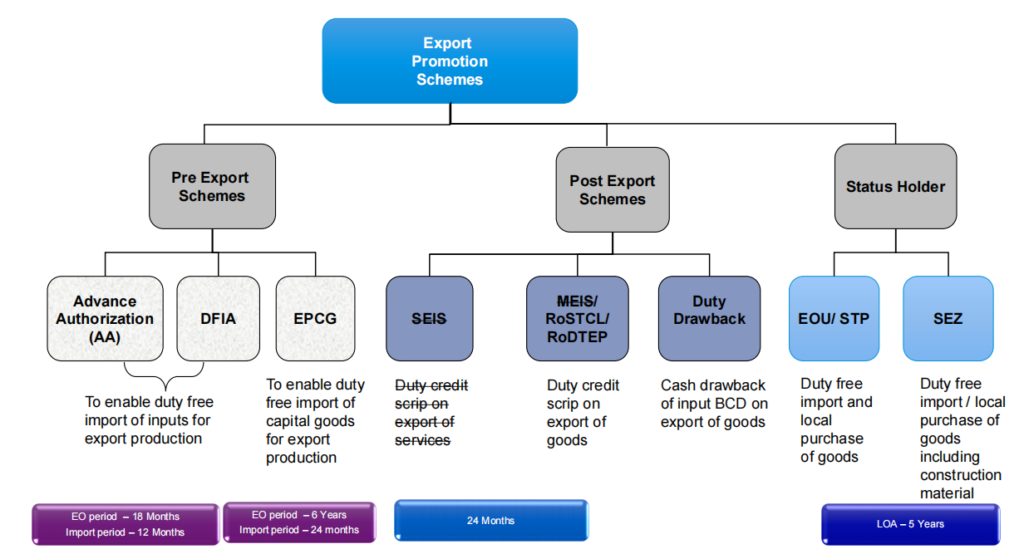
5. Advance Authorisation
Objective
- To allow the duty free import of input, required for manufacture of export product
Coverage
- Manufacturer exporters or merchant exporter tied to supporting manufacturer
Entitlement
- Import of inputs allowed on the basis of SION (or ad-hoc norms)
- AdvanceAuthorization for Annual requirement allowed to exporters with export performance in at least preceding two financial years
- CIF value of imports can be up to 300% of the physical export and/or FOR value of deemed export in preceding financial year or Rs. 1 Crore, whichever is higher
Benefits
- Imports exempted from Basic Customs duty, IGST, Additional Customs Duties, SWS, Anti-dumping Duty, Safeguard Duty
Other Key points
- Imports subject to Actual user condition
- Minimum 15% value addition required on inputs
- Export obligation period 18 months (extendable up to another 12 months)
6. Export Promotion Capital Goods Scheme (‘EPCG’)
Objective
- To facilitate the duty free import of capital goods for export production
Coverage
- Manufacturer exporters with or without supporting manufacturers, merchant exporters tied to supporting manufactures and service providers
Entitlement
- Import of capital goods required for manufacture of export goods or services
- Import of spares, mould, dies etc. also allowed
Benefits
- Exemption from Customs duty on import
- Refund of IGST on local procurements
Other Key points
- Actual user condition till the completion of export obligation
- Export obligation equal to 6 times of duty saved to be achieved in 6 years
- Exports above average of last three years exports are only counted for EO under EPCG
- In case of domestic procurement, EO shall be 25% of applicable specific EO
- Waiver of part EO in case of early fulfilment of substantial EO
7. Relevant changes under AA and EPCG under FTP 2023

- Benefits of Self-ratification Scheme for fixation of Input-Output Norms extended to 2 star and above status holders in addition to Authorized Economic Operators at present.
- Reduced EO for EPCG for Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) of all types, Vertical Farming equipment, Wastewater Treatment and Recycling, Rainwater harvesting system and Rainwater Filters and Green Hydrogen.
- Dairy sector to be exempted from maintaining Average EO – to support dairy sector to upgrade the technology.
- Special AA Scheme extended to export of Apparel and Clothing sector under para 4.07 of HBP on self-declaration basis to facilitate prompt execution of export orders. Norms would be fixed within fixed timeframe.
8. Duty Drawback
Objective
- To allow reimbursement of the ‘notional’ Basic Customs duty suffered on inputs/input services used for import/manufacture of products intended to be exported
Coverage
- Manufacturer exporters or merchant exporter
Entitlement
- Cash refund of notional Basic Customs Duty on inputs used in export product
- Drawback is granted at a rate (specified by Government) of FOB value of export
- If rate fixed by Government reimburses less than 80% of actual duty then exporter can seek special brand rate for his product
Other Key Points
- Duty drawback not available on exports of EOU, SEZ, Advance authorisation etc.
- Fixation of brand rates take significant time
- Drawback amount cannot be more than market value of the product
9. Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Products (RoDTEP)
- Cabinet approved the RoDTEP to replace the MEIS (March 2020)
- Incentive as a percentage of the FOB value of export
- Implementation with end to end digitization
- Monitoring and audit mechanism with IT based Risk Management System (RMS)
- Objective of RoDTEP is to make Indian exports cost competitive to International Markets
- Rates on the basis of actual taxes suffered but not reimbursed
10. Taxes/duties remitted under RoDTEP
- VAT & ED on fuel used in self incurred transportation costs
- VAT and ED used in generation of electricity via power plants or DG sets
- VAT and ED on fuel used in running of machineries/plant
- Electricity duty on purchase of electricity
- Stamp duty on export documents
- Mandi Tax/Municipal Tax/Property Tax
- Blocked GST ITC under Section 17(5)
- Blocked GST due to defaults of suppliers (mismatch of ITC, Section 16(2) & 16 (4)
11. Points to be noted
1. What happens if intention to avail benefit under RoDTEP is not declared in Shipping Bill?
ICEGATE advisory states that benefit would not be available. Appeal may be filed for amendment of free SB to RoDTEP
2. Can EPCG or duty drawback scheme be claimed simultaneously along with RoDTEP?
Yes. No specific restriction under the Scheme
3. Can unlimited benefits on goods exported be claimed or is there a ceiling?
Scheme is under overall budget outlay-indication that there could be ceiling on max. benefit within the overall budget
4. Whether benefit can be claimed if consideration is received in INR?
No. In certain cases, payment received in INR is considered equivalent to forex
5. Factory has MOOWR license – Is benefit under RODTEP available?
Yes. Products manufactured wholly or partly in a warehouse under Section 65 of the Customs Act, 1962 are ineligible
6. What to do if excess scrips have been credited to the exporter?
Similar to duty drawback, surrender back excess amount
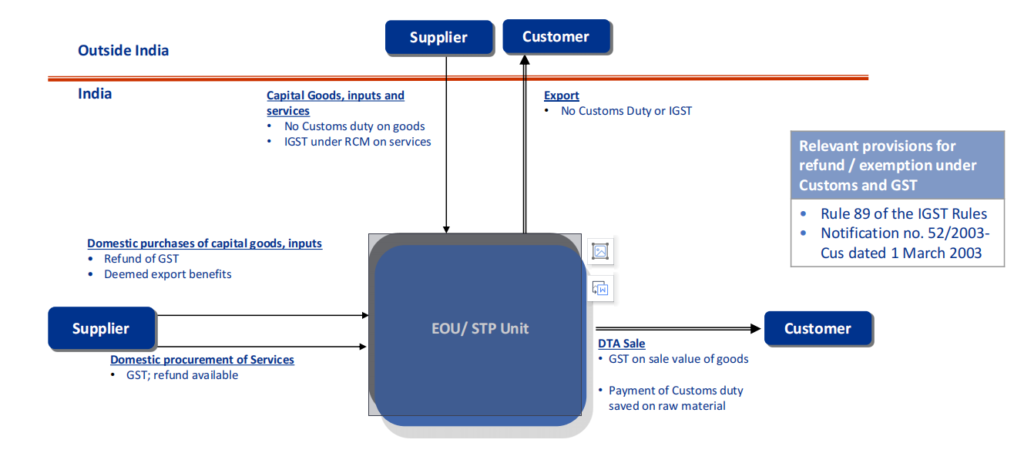
12. EOU/STP Scheme – Overview and Features
- IGST exemption on imports extended sine die vide Notification no. 37/2022-Cus dated 30 June, 2022
- Unlike SEZ, Authorities not demanding import licence on local sale of laptops or other electronic items
- Liberal Business Contingency Plan guidelines
- Liberal Work from Home guidelines
Objective
- To provide specific incentives, internationally competitive and conducive environment for exports
Coverage
- Manufacturer exporters and service providers; trading not allowed
Entitlement
- Import of capital goods required for manufacture of export goods or services
- Import of raw material, packing material, fuel, spares, mould, dies etc. also allowed
Benefit
- Exemption from Customs duty on import of raw material, consumables and capital goods
- Refund of IGST on local procurement of goods
- Deemed export drawback on local procurements
Other Key Points
- Sharing of facilities with SEZ not permitted
- No Corporate tax benefit
- Import of restricted goods allowed without authorizations
13. EOU/STP Scheme – Taxes on supply chain
14. Status Holder (‘SH’) Scheme
| Key aspects | Particulars |
| Objective | To grant privileges to exporters with high export performance |
| Eligibility |
|
| Privileges |
|
| Status Category | |||
| Under erstwhile FTP | Under FTP 2023 | ||
| Threshold export performance to be achieved in during current and previous three financial years | Threshold export performance to be achieved in during current and previous three financial years | ||
| Status Category | Exports Performance FOB/FOR Value (in US $ million) | Status Category | Exports Performance FOB/FOR Value (in US $ million) |
| One Star Export House | 3 | One Star Export House | 3 |
| Two Star Export House | 25 | Two Star Export House | 15 |
| Three Star Export House | 100 | Three Star Export House | 50 |
| Four Star Export House | 500 | Four Star Export House | 200 |
| Five Star Export House | 2000 | Five Star Export House | 800 |
| Export performance is necessary in at least two out of four years
For deemed exports, FOR value shall be converted into US $ at the exchange rate notified by CBIC as on 01 April each year. |
Export performance is necessary in all the three financial years
For deemed exports, FOR value shall be converted into US $ at the exchange rate notified by CBEC as on 01 April each year. |
||
| Validity- 5 Years | |||
15. Clubbing of various schemes
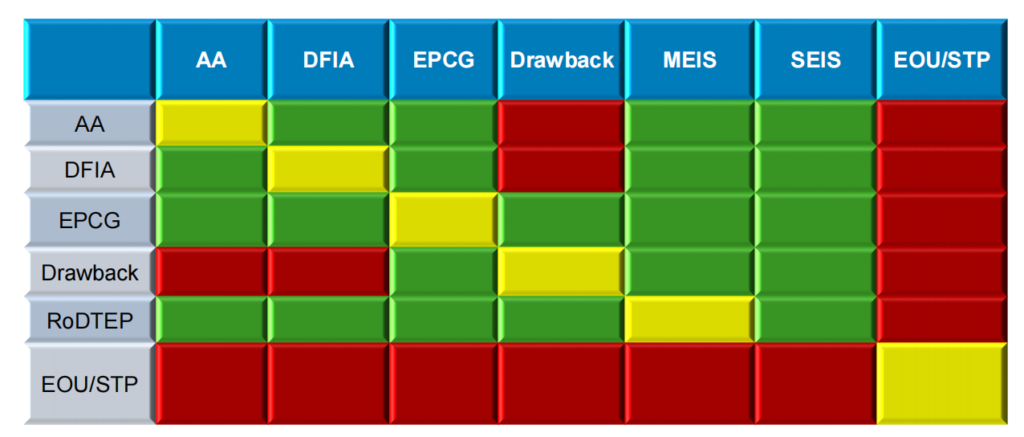
16. Deemed Export
- Certain specified supplied regarded as deemed export even though goods do not leave the country and payment is received in INR
- Deemed export as per GST law are the supplies specified by notification issued under Section 147 of CGST Act, 2017
- Under FTP and GST law, supplies to AA, EPCG, EOU/STP/BTP scheme holders eligible as deemed export
- In addition under FTP, supplies to specified projects eligible for deemed export benefit
- Under GST law, refund of GST available post supply
- Under FTP, deemed export drawback (AIR) and refund of terminal excise duty available; granted by DGFT
- In addition, AA may also be issued for supplies to deemed export category
17. Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies (SCOMET)
- India signatory to International conventions on disarmament and non-proliferation
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1540 obliges all countries to prohibit access of weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems to non-state actors (in particular for terrorist purposes)
- India is also member of major multilateral export control regimes like Missile Technology Control Regime, Wassenaar Agreement and Australia Group
- India formulated Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005 which regulates export, transfer, re-transfers, brokering in specified goods, technology and services
- Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies or SCOMET now part of FTP; earlier only part of ITC (HS)
18. SCOMET
- India’s export control list specifies items and technology which have dual use – civil as well as military
- Export of items mentioned in SCOMET list allowed only with the approval of DGFT or other authorities
- Exporter need to self declare in the shipping bill if export item covered in SCOMET list
- Non-compliance attracts penal provisions under Customs Act, 1962 and FTDRA, 1992
- Products grouped under total 8 chapters
| SCOMET Category | SCOMET Items | Jurisdictional Licensing Authority | Remark |
| 0 | Nuclear materials, nuclear-related other materials, equipment and technology | Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) | Including items mentioned in Note 2 of CIN of SCOMET List |
| 1 | Toxic chemical agents and other chemicals | Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) | |
| 2 | Micro-organisms, Toxins | DGFT | |
| 3 | Materials, Materials Processing Equipment and related Technologies | DGFT | |
| 4 | Nuclear-related other equipment and technology, not controlled under Category ‘0’ | DGFT | |
| 5 | Aerospace systems, equipment, including production and test equipment, and related Technology and specially designed components and accessories thereof. | DGFT | |
| 6 | Munitions List | Department of Defence Production (DDP)/Ministry of Defence Excluding those covered under Note 2 and 3 of CIN and Sub-category 6A007, 6A008 | Department of Defence Production (DDP)/ Ministry of Defence
Excluding those covered under Note 2 and 3 of CIN and Sub-category 6A007, 6A008 |
| 7 | ‘Reserved’ | DGFT | |
| 8 | Special Materials and Related Equipment, Material Processing, Electronics, Computers, Telecommunications, Information Security, Sensors and Lasers, Navigation and Avionics, Marine, Aerospace and Propulsion. | DGFT |
19. Amnesty Scheme
- An Amnesty Scheme vide Public Notice 2/2023 dated 1 April 2023 Announced
- Scheme covers only default under Advance and EPCG authorization
- Scheme does not cover defaults under other schemes like EOU, STPI, duty drawback etc.
- Default in export obligation only covered under the scheme
- AA and EPCG authorizations issued under FTP 2009-14 till 31.03.2015 covered
- AA and EPCG issued under previous FTP covered only when EO period valid beyond 12.08.2013
- Advance and EPCG authorizations issued under FTP 2015-20 not covered
- All duties in proportion to unfulfilled EO need to be paid back
- Interest amount capped to 100% of basic duty amount
- No interest payable on Additional Customs Duty and Special Additional Customs duty
- Substantial saving of interest possible
- CVD and SAD paid under Amnesty scheme cannot be claimed as credit or refund
- Application needs to be filed DGFT by 30.06.2023 and payment of duties by 30.09.2023
- Application to be filed in an application form given at DGFT portal
- In case of 100% default in EO; pay duty and interest and then approachDGFT
- In case of partial default, DGFT will suggest the amount payable after examination
- Payments already made for closure of authorization not eligible for refund
- Cases pending under adjudication or appeal may be closed under the scheme
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied






 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
