Introduction to Overseas Investments in Foreign Entities
- Blog|FEMA & Banking|
- 12 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 1 August, 2023

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Brief About the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 [FEMA, 1999]
- Capital and Current Account Transactions
Check out Taxmann's Overseas Investment Ready Reckoner which is the first and only resource dedicated to overseas investment. It delves into meticulous detail, featuring an array of practical examples, instructive case studies, and compounding orders. The author has strived to maintain simplicity while ensuring the book is exhaustive and practically beneficial.
1. Introduction
Overseas investments in foreign entities have been recognised as important avenues for promoting global business by Indian entrepreneurs. It is perceived as a medium of economic and business cooperation between India and other countries. Transfer of technology and skill, sharing of results of R&D, access to wider global market, promotion of brand image, generation of employment and utilisation of raw materials available in India and the host country are significant benefits arising from such overseas investments. They are also important drivers of foreign trade through increased exports of plant and machinery and goods and services from India and a source of foreign exchange earnings through dividend earnings, royalty, technical know-how fee and other entitlements on such investments.
Overseas investments enhance the scale and scope of business operations by providing global opportunities for growth and diversifying the risk, increase the competitiveness of Indian entities and boost their brand value through easier access to technology, research and development, a wider global market and reduced cost of capital.
As per the data available on RBI website as on 15th Feb., 2023, there are 529 entities which have made investment outside India in the month of Jan., 2023 amounting to financial commitment of more than 1353 million USD.
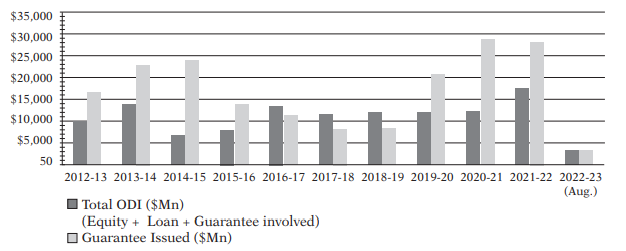
Over time, the trade openness of countries across the globe has been increasing as measured by trade as a proportion of GDP. As per the Economic Survey Report 22-23, for the world as a whole, the share of trade as a percentage of world GDP has been in the range of 50-60 per cent since 2003 and stood at 52 per cent in 2020, according to the World Bank database. For India as well, the share of trade as a percentage of GDP has been steadily increasing, being above 40 per cent since 2005 (except 2020 being the pandemic year). The ratio stands at 46 per cent in 2021 and 50 per cent for H1 of 2022.
As per Monthly Fact Sheet (February 2023) ODI data published by Department of Economic Affairs, Central Government the cumulative amount of actual ODI outflows for the period from April 2000 to February 2023 have been as depicted below:
(Figures in US$ Million)
|
Sr. No. |
CUMULATIVE AMOUNT OF ACTUAL ODI OUTFLOWS | Total | ||
| 1. | Equity | Loans | Guarantee Invoked |
Equity + Loans + Guar- antee Invoked |
| Period (from April, 2000 to February, 2023) |
1,91,858 |
92,587 | 6.658 |
2,91,103 |
|
2. |
CUMULATIVE AMOUNT OF ODI (FINANCIAL COMMITMENT) |
Equity + Loans + Guar- antee Issued |
||
| Period (from April, 2000 to February, 2023) |
Equity |
Loans | Guarantee Issued | |
| 1,91,858 | 92,587 | 3,78,509 |
6,62,954 |
|
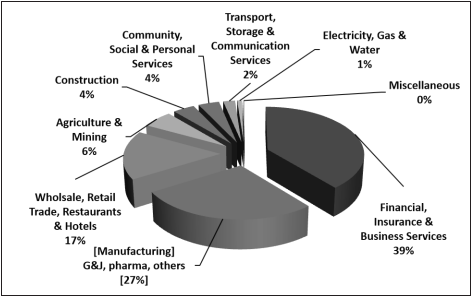
It is not only big companies but also mid size and small entities which are now exploring the global markets and as can be seen from the figure below investment are made across the sectors:
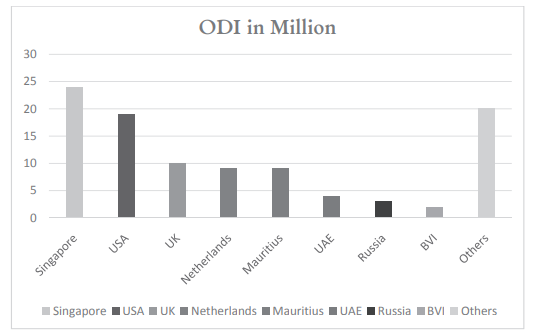
Investments have been made in jurisdictions all across the globe from Singapore, USA, UK, Netherlands, etc.
Major objectives of overseas investment is tax structuring, risk diversification, business expansion, etc. These overseas investments are very important drivers of foreign trade and technology transfer thereby boosting employment, investment and growth through such interlinkages. The chart below shows the investment made in various countries by Indian residents.
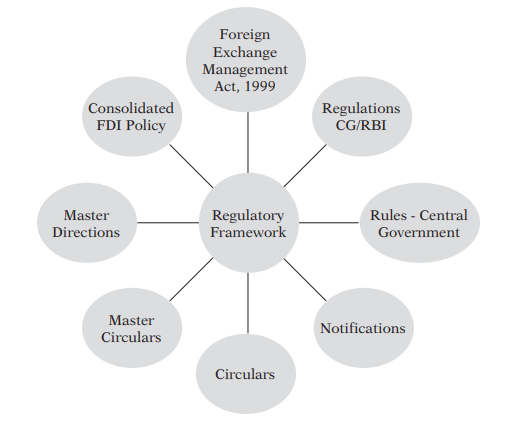
Any transaction involving Foreign exchange is governed under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 [“FEMA”/“The Act”]. This chapter deals with complete framework of FEMA so that the topic of Overseas Investment [which is the subject matter of this book] can be build from basic.
2. Brief About the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 [FEMA, 1999]
All transactions involving foreign exchange are governed by the Act enacted by parliament called the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 [FEMA, 1999]. The key motive of the Act is to manage and promote the dealings in foreign exchange with an objective of facilitating external trade and payments along with promotion of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India.
FEMA Consist of total 49 sections, out of which first 9 sections are substantive and the rest are procedural or administrative. The power of enforcement of FEMA is given to Central Government (CG) and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under sections 46 and 47 respectively. CG handles acts and rules of FEMA whereas the RBI handles procedural and administrative aspects of FEMA.
Keeping in view the current requirements, the Government and RBI from time to time comes up with new regulations and amendments/changes in the existing ones through Orders/Allied Rules, Press Notes, Circulars, etc. The regulatory framework over a period of time thus consists of Act, Regulations, Press Notes, Press Releases, Clarifications, etc.
2.1 Rules
As per section 46 of the Act, the Central Government may, by notification, make rules to carry out the provisions of FEMA, 1999. Inter alia, such rules may provide for:
(a) the imposition of reasonable restrictions on current account transactions under section 5;
1[(aa) the instruments which are determined to be debt instruments under sub-section (7) of section 6;
(ab) the permissible classes of capital account transactions in accordance
with sub-section (2A) of section 6, the limits of admissibility of foreign exchange, and the prohibition, restriction or regulation of such transactions;]
(b) the manner in which the contravention may be compounded under sub-section (1) of section 15;
(c) the manner of holding an inquiry by the Adjudicating Authority under sub-section (1) of section 16;
(d) the form of appeal and fee for filing such appeal under sections 17 and 19;
(e) the salary and allowances payable to and the other terms and conditions of service of the Chairperson and other Members of the Appellate Tribunal and the Special Director (Appeals) under section 23;
(f) the salaries and allowances and other conditions of service of the officers and employees of the Appellate Tribunal and the office of the Special Director (Appeals) under sub-section (3) of section 27;
(g) the additional matters in respect of which the Appellate Tribunal and the Special Director (Appeals) may exercise the powers of civil court under clause (i) of sub-section (2) of section 28;
2[(gg) the aggregate value of foreign exchange referred to in sub-section (1) of section 37A;]
(h) the authority or person and the manner in which any document may be authenticated under clause (ii) of section 39; and
(i) any other matter which is required to be, or may be, prescribed.
The Central Government has notified following rules as given below:
1. FEM (Encashment of Draft Cheque, Instrument and Payment of Interest) Rules, 2000.
2. FEM (Authentication of Documents) Rules, 2000.
3. FEM (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000.
4. FEM (Adjudication Proceedings and Appeal) Rules, 2000.
5. FEM (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2000.
6. Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019.
7. Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Rules, 2022.
These Rules are briefly described below:
(1) Foreign Exchange Management (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2000
The Foreign Exchange (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2000 deal with manner of compounding of offences. These rules prescribe the authority according to the amount involved in offence with which Compounding application is to be filed and procedure of compounding along with other matters.
(2) Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000
The Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000 deal with drawal of foreign exchange for current account transaction. These rules divided the current account transaction in three schedules.
Transactions specified in Schedule I are transactions which are prohibited and cannot be undertaken, Transaction in Schedule II and Schedule III is allowed with the prior approval of the Central Government and Reserve Bank of India, respectively. The Rules specify that if transaction are made through Resident Foreign Currency (RFC) Account or Exchange, Earners’ Foreign Currency (EEFC) Account of the remitter, then these rules are not applicable.
(3) Foreign Exchange (Authentication of Documents) Rules, 2000
The Foreign Exchange (Authentication of Documents) Rules, 2000 deal with authorisation of documents to be affixed, impressed or submit which are received from outside India and it also defines the eligibility of person authorised to authenticate the documents.
(4) Foreign Exchange Management (Adjudication Proceedings and Appeal) Rules, 2000
The Foreign Exchange Management (Adjudication Proceedings and Appeal) Rules, 2000 define the hierarchy of Adjudicating authority and delegate the power to the Central Government to appoint the officers for holding the inquiry under Chapter IV of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and deal with the procedure and time limits to proceed with the inquiry. These rules also define the procedure to file appeal with the special director and Appellate tribunal.
(5) Foreign Exchange Management (Encashment of Draft, Cheque, Instru- ment and Payment of Interest) Rules, 2000
The Foreign Exchange Management (Encashment of Draft, Cheque, Instrument and Payment of Interest) Rules, 2000 define the authorisation to deliver the draft, cheque and other instruments for encashment which are under investigation, with the prior approval of the RBI and also provide the procedure to encash the above-mentioned instruments.
(6) Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019
In exercise of the powers conferred under section 46(2)(aa) and (ab) of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and in supersession of the Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of Security by a Person Resident outside India) Regulations, 2017 and the Foreign Exchange Management (Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property in India) Regulations, 2018, the Central Government issued Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019.
(7) Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Rules, 2022
Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Rules, 2022 were notified by the Central Government vide Notification No. G.S.R. 646(E) dated August 22, 2022 in supersession of the Notification No. FEMA 120/2004-RB dated July 7, 2004 [Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of any Foreign Security) (Amendment) Regulations, 2004] and Notification No. FEMA 7 (R)/2015- RB dated January 21, 2016 [Foreign Exchange Management (Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property Outside India) Regulations, 2015].
2.2 Regulations
Section 47 of the FEMA empowers the RBI to make regulations to carry out the provisions of FEMA, 1999.
Such regulations may provide for:
(a) For Capital Account transaction:
-
- the permissible classes of capital account transactions,
- the limits of admissibility of foreign exchange for such transactions,
- and the prohibition, restriction or regulation of certain capital account transactions under section 6;
(b) the manner and the from in which the declaration is to be furnished under clause (a) of sub-section (1) of section 7;
(c) the period within which and the manner of repatriation of foreign exchange under section 8;
(d) the limit up to which any person may possess foreign currency or foreign coins under clause (a) of section 9;
(e) the class of persons and the limit up to which foreign currency account may be held or operated under clause (b) of section 9;
(f) the limit up to which foreign exchange acquired may be exempted under clause (d) of section 9;
(g) the limit up to which foreign exchange acquired may be retained under clause (e) of section 9;
(h) export, import or holding of currency or currency notes;
(i) any other matter which is required to be, or may be specified.
The Central Government and Reserve Bank have, by various notifications, issued the following regulations:
- Foreign Exchange Management (Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property in India) Regulations, 2000 subsumed in Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property Outside India) Regulations, 2015 subsumed in Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Rules, 2022 w.e.f. 22 August, 2022.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Borrowing and Lending in Rupees) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Borrowing or Lending in Foreign Exchange) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations, 2016.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Establishment in India of Branch Office or Liaison Office or Project Office or Office or Other Place of Business) Regulations, 2016.
- Foreign Exchange Management(Export and Import of Currency) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Export of Goods and Services) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Foreign Currency Accounts by a Person Resident in India) Regulations, 2016.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Foreign Exchange Derivative Contracts) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Guarantees) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Insurance) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Investment in Firm of Proprietary Concern in India) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Issue of Security in India by a Branch, Office or Agency of a Person Resident Outside India) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Manner of Receipt and Payment) Regulations, 2016.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Offshore Banking Unit) Regulations, 2002.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Permissible Capital Account Transactions) Regulations, 2000.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Possession and Retention of Foreign Currency) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Realisation, Repatriation and Surrender of Foreign Exchange) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Remittance of Assets) Regulations, 2016.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of any Foreign Security) Regulations, 2004 subsumed in Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Rules, 2022 w.e.f. 22 August, 2022.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of Security by a Person Resident Outside India) Regulations, 2017 subsumed in Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019.
- Foreign Exchange Management [Withdrawal of General Permission to Overseas Corporate Bodies (OCBs)] Regulations, 2003.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Crystallization of Inoperative Foreign Currency Deposits) Regulation, 2014.
- Foreign Exchange Management (International Financial Services Centre) Regulation, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Regularization of Assets held Abroad by a Person Resident in India) Regulations, 2015.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Debt Instruments) Regulations, 2019.
- Foreign Exchange Management (Overseas Investment) Regulations, 2022.
Apart from Rules, Regulations there are A.P. DIR. (Series) Circulars which are issued by RBI as the administrative and procedural instructions to Bank.
These A.P. DIR. (Series) Circulars use to get consolidated and issued as Master Circulars by RBI every July till Jan. 2016. Effective Jan. 2016 Master circulars have been discontinued. The existing set of Master Circulars issued on various subjects stands withdrawn. So any reference to the Master circular on the subject matter is no more valid.
2.3 Master Directions
The RBI has started issuing Master Directions on all regulatory matters beginning in January 2016. The Master Directions consolidate instructions on rules and regulations framed by the Reserve Bank under various Acts including banking issues and foreign exchange transactions. The process of issuing Master Directions involves issuing one Master Direction for each subject matter covering all instructions on that subject. Any change in the rules, regulations or policy is communicated during the year by way of circulars/press releases. The Master Directions are updated suitably and simultaneously whenever there is a change in the rules/regulations or there is a change in the policy. The existing set of Master Circulars issued on various subjects stands withdrawn with the issue of the Master Direction on the subject.
Few of the master Directions being issued are:
- Master Direction – Export of Goods and Services.
- Master Direction – Money Changing Activities.
- Master Direction – Opening and Maintenance of Rupee/Foreign Currency Vostro Accounts of Non-resident Exchange Houses.
- Master Direction – External Commercial Borrowings, Trade Credit, Borrowing and Lending in Foreign Currency by Authorised Dealers and Persons other than Authorised Dealers.
- Master Direction – Miscellaneous.
- Master Direction – Reporting under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
- Master Direction – Import of Goods and Services.
- Master Direction – Direct Investment by Residents in Joint Venture (JV)/ Wholly Owned Subsidiary (WOS) Abroad.
- Master Direction – Deposits and Accounts.
- Master Direction – Remittance of Assets.
- Master Direction – Acquisition and Transfer of Immovable Property under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
- Master Direction – Establishment of Liaison/Branch/Project Offices in India by Foreign Entities.
- Master Direction – Insurance.
- Master Direction – Other Remittance Facilities.
- Master Direction – Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS).
- Master Direction – Borrowing and Lending transactions in Indian Rupee between Persons Resident in India and Non-Resident Indians/Persons of Indian Origin.
- Master Direction – Compounding of Contraventions under FEMA, 1999.
As far as Overseas investments are concerned the regulatory framework is as follows:
| Act | Rules | Regulations | Directions |
FAQ |
|
|
|
|
|
It is pertinent to note here that only the Rules issued in exercise of the powers vested in the Central Government under section 46 of the Act and regulations made under section 47 of the Act constitute the law with regard to overseas investment under FEMA. The FEMA notifications issued by the Central Government and RBI to amend such law constitute amendments which modify the law. AP DIR circulars, FAQs, master directions do not constitute “law”. These are directions to authorised persons or are clarificatory in nature for ease of reference and is not equivalent to law. However, they certainly have
persuasive value.
3. Capital and Current Account Transactions
To understand any transaction involving Foreign exchange it is essential to understand the type of transaction. All the foreign exchange Transactions are divided into two categories:
- Current Account Transactions
- Capital Account Transactions
In order to understand current and capital account transactions under FEMA, it is important to consider the following aspects:
- Definition: It is necessary to comprehend the meaning of both terms (i.e. Capital and Current account transactions) and how they are defined in the Act.
- Characterisation: Determining the nature of the transaction is crucial in determining whether it falls under the current account or capital account category.
- Allowability: It is important to ascertain whether the transaction is allowed to be undertaken and if so, whether it is subject to any restrictions.
General rule with respect to Current and Capital account transactions:
As a general rule, all the current account transactions under FEMA,1999 are permitted (except those specified) and all the capital account transactions are prohibited or regulated (except those specified).
- All current account transactions are allowed until prohibited
- All capital account transactions are prohibited until permitted
To execute any transaction involving Foreign Exchange, it is important to differentiate the same in either current account transaction or capital account transaction.
- Ins. by Finance Act, 2015 (20 of 2015), dated 14-5-2015 and effective from 9th day of September, 2015.
- Ins. by Finance Act, 2015 (20 of 2015), dated 14-5-2015 and effective from 9th day of September, 2015.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied





 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
