India’s Shift to Faceless Income Tax Assessment
- Blog|Income Tax|
- 6 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 15 January, 2024

Table of Contents
- Background
- What is Faceless Assessment?
- Features of Faceless Assessment Scheme
- Authorities Responsible for Conducting Faceless Assessment
- Procedure of Faceless Assessment Conducted by NFAC
- Some Important Points related to Faceless Assessment
- Conclusion
1. Background
The government has been involved in the process of entire digitization of the Income Tax since long time. As a part of the same, the assessment proceedings too were in the process of being faceless; initially, they were converted into electronic proceedings. In the speech of 2018-19 budget, the finance minister mentioned that E-assessment was introduced in the year 2016 on a pilot basis, and in 2017 it was extended to 102 cities, with an objective of reducing the interface between the department and the taxpayers.
The experience gained by the government between the period 2016 to 2018 was sufficient to rollout the scheme of E-assessment throughout the country. The age-old assessment procedure of the income tax department was transformed, and the manner in which the taxpayers/stakeholders communicated with the department was changed. It was proposed to notify the scheme of assessment, where the same could be done in electronic mode. Thus, the e-assessment scheme was introduced in the Union Budget 2019, prior to the elections, with an objective to make greater efficiency in the assessment proceedings.
It was in the second budget of 2019, after the elections, that faceless assessment scheme was introduced. It was mentioned in the said budget speech, that the then existing system of scrutiny assessment in the income tax department involved a high level of interaction between the taxpayer and department, leading to certain undesirable practices on the part of the tax officials. Thus, the tax officials were directly alleged that they were engaged in some undesirable practices. So, to eliminate such instances, the scheme of faceless assessment involving no human interface was proposed to be launched in a phased manner.
2. What is Faceless Assessment?
Faceless Assessment means assessing taxpayers in a way where they do not visit the Income Tax Department and do not come face-to-face/in direct contact with any of the Income Tax officials.
Faceless Assessment Scheme was introduced in India with effect from 1st April, 2021, with the primary objective of elimination of human interface in the direct taxation functioning of the country and introduction of widespread adoption and usage of data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI). However, the most salient feature of this scheme was the introduction of team-based assessment with dynamic jurisdiction which replaced the conventional territorial/jurisdiction-based assessment.
3. Features of Faceless Assessment Scheme
Faceless Assessment Scheme possesses the following features:
- No Human Interface
- Expeditious Disposal of Cases
- Ease of Compliance for TaxPayers
- Transparency and Efficiency
- Functional Specialisation
4. Authorities Responsible for Conducting Faceless Assessment
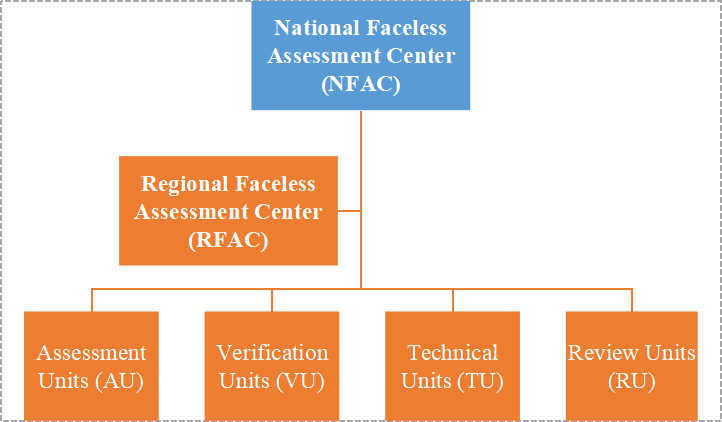
4.1 National Faceless Assessment Center (NFAC)
- NFAC is basically the centralized proceeding center that conducts faceless assessments PAN India (all across India).
- The person in-charge of NFAC is the Principal Chief Commissioner/Principal Director General of the Income Tax.
- Every type of communication between units and assesses is processed through this centralized NFAC.
- It sends notices and receives response from the Assessees over virtual mode and transfers the documents to the required units for further assessment.
4.2 Regional Faceless Assessment Center (RFAC)
- RFAC plays a crucial role in assisting the NFAC and ensuring the smooth functioning of assessment procedures within specific regions.
- Each RFAC comprises of a number of Assessment Units, Verification Units, Review Units and Technical Units.
- NFAC may allocate the task of assessment, verification, review or technical assistance randomly, related to any case to the RFAC of any region, through an automated allocation system.
4.3 Responsibilities of Assessment Units (AU)
AU is the unit of Assessing Officers that lead all the assessments indirectly. They perform the function of making assessments, however, all communication is delivered through the NFAC. But AU is the unit that prepares all relevant documents and verification with the questionnaires. Duties performed by AU are as follows:
- Identification of points or issues material for the determination of any liability (refund) or referred for Faceless Assessment.
- Analysis of the material furnished by Assessee.
- Seeking information or clarification on points or issues so identified.
4.4 Responsibilities of Verification Units (VU)
VU is the unit that verifies the documents provided by the assesse through the filing of the returns and replies against notices.
- VU is the unit that performs the function of providing verifications which include enquiry, cross verification, examination of the book of accounts, and data response by the Assessee.
- It verifies the data provided by the assessees through their returns as well as a comparison of the same with the data available at other portals.
- Examination of witness and recording of the statement.
4.5 Responsibilities of Technical Units (TU)
TU is the unit that provides technical assistance in the Faceless Assessment procedure. It is used to authenticate the information with the help of technology. Such units are the experts in artificial intelligence.
- They are involved in faceless assessments to complete technical verifications including advise on legal accounting, valuation of property and transfer pricing.
- Forensic analysis, information technology.
- Data analytics and legal technical report for the assessments.
4.6 Responsibilities of Review Units (RU)
Before finalization of the order, these units are involved to review all the aspects of the faceless assessment. NFAC can take suggestions from the RU before finalizing the order.
- RU reviews the relevant material evidence that has been brought to records.
- RU reviews the facts and laws which have been duly incorporated for the assessment.
- The unit also addresses whether the issues require additions or not.
- Also, it verifies if the disallowance has been incorporated or not.
5. Procedure of Faceless Assessment Conducted by NFAC
The procedure of faceless assessment involves the following steps:
- NFAC assigns the case to a specific AU under any RFAC through Automated allocation.
- Notice prepared by the Assessment Unit (AU) is delivered to Assessee through National Faceless Assessment Center (NFAC).
- Assessee is required to file response or provide further information as required by the AU.
- AU places a request for conducting enquiry/verification to the Verification Unit (VU) through NFAC.
- Request for seeking technical assistance by Technical Unit (TU) is assigned by AU through NFAC.
- Income Loss determination by AU.
- AU issues Show Cause Notice (SCN) to the Assessee through NFAC.
- Assessee to file response to the Show Cause Notice (SCN).
- Making of draft assessment order by the AU and review of the same by Review Unit (RU).
- Review Report prepared by the RU is forwarded to AU.
- Completion of the Assessment by the AU.
6. Some Important Points related to Faceless Assessment
- All communication related to faceless assessment, among the AU, VU, RU and TUwith the assesse shall be through NFAC or RFAC only.
- All internal communicationand exchange of databases/documents/evidence will be done through electronic mode
- Any database/document/evidence related to faceless assessment shall be authenticated by way of electronic communication, digital signature and electronic verification code.
- In case of personal hearing, it shall be conducted through video conferencing and telecommunication.
- Orders/notices/other electronic communication shall be delivered to the assesse via E-mails/mobile alerts (on Real Time Basis)/registered account available on the Income tax portal.
- Assessee shall file his/her response to any notices/questionnaire through his/her registered account.
- Once the acknowledgement is sent by the NFAC, the response shall be authenticated.
- The assesse shall not be required to appear physically or through any other representative in connection with the assessment proceedings.
- An oral submission is allowed in case of clarification against show cause notice against the Income and Loss Determination proposal.
7. Conclusion
Thus, in faceless assessment, all communication with taxpayers being done electronically, identity of the assessing officers remains unknown. Further, earlier the taxpayers were required to make multiple visits to the Income Tax office, which involved allegations and some incidences of discretion and subjective approach, resulting in high-pitched assessments. Now, the Faceless Assessment Scheme in Income Tax proceedings has paved way for easier compliances, faster assessments and lower disputes which is evident from the fact that in past few years, tax scrutiny cases in the country have reduced from 0.71% to 0.25% due to the assessment selection process being transformed from manual to automated, based on data analytics and artificial intelligence.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied




 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
