Guide to Financial Services Organization and its Registration Process
- Blog|FEMA & Banking|
- 13 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 4 August, 2022

Table of Contents
1. Financial Services Organization Structure in India
2. Categorization of the different types of NBFCs
3. Benefits of incorporating NBFC
4. Incorporation of NBFCs and registration process with RBI
5. Registration process with Reserve Bank of India
6. Procedure for filing application with Reserve Bank of India
8. Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC)
9. Micro Finance Institutions (MFI)
10. Nidhi Companies
11. Payment Banks
Checkout Taxmann's Setting Up of Business Entities and Closure (SUBEC) | QUICK REVISION CHARTS which covers the subject matter in a summarised tabular chart format with point-wise summaries, etc. It incorporates all the latest applicable provisions and amendments. CS-Executive | New Syllabus | Dec. 2022 Exams
1. Financial Services Organization Structure in India
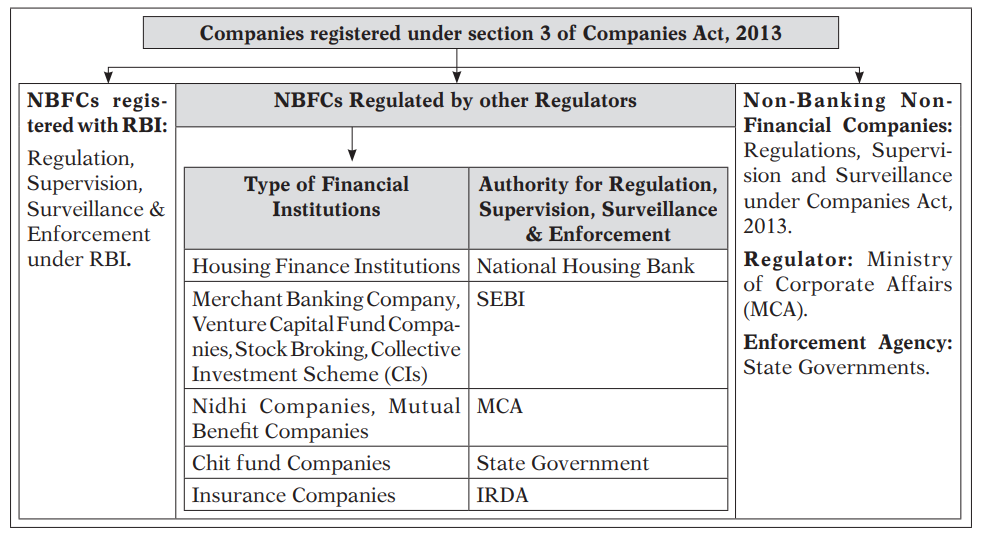
2. Categorization of the different types of NBFCs
(Note: The list is inclusive not exclusive)
2.1 Asset Finance Company (AFC)
AFC is a company which is a financial institution carrying on as its principal business the financing of physical assets supporting productive/economic activity, such as automobiles, tractors, lathe machines, generator sets, earth moving and material handling equipments moving on own power and general purpose industrial machines.
2.2 Investment Company (IC)
IC means any company which is a financial institution carrying on as its principal business the acquisition of securities.
2.3 Loan Company (LC)
LC means any company which is a financial institution carrying on as its principal business the providing of finance whether by making loans or advances or otherwise for any activity other than its own but does not include an Asset Finance Company.
2.4 Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)
IFC is a non-banking finance company :
-
- which deploys at least 75 per cent of its total assets in infrastructure loans.
- has a minimum Net Owned Funds of ` 300 crore
- has a minimum credit rating of ‘A’ or equivalent
- CRAR of 15%.
2.5 Non-Banking Financial Company – Factors (NBFC-Factors)
NBFC-Factor is a non-deposit taking NBFC engaged in the principal business of factoring. The financial assets in the factoring business should constitute at least 50 per cent of its total assets and its income derived from factoring business should not be less than 50 per cent of its gross income.
2.6 Mortgage Guarantee Companies (MGC)
MGC are financial institutions for which at least 90% of the business turnover is mortgage guarantee business or at least 90% of the gross income is from mortgage guarantee business and net owned fund is `100 crore.
2.7 NBFC- Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC)
Financial institution through which promoter/promoter groups will be permitted to set up a new bank. It’s a wholly-owned Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC) which will hold the bank as well as all other financial services companies regulated by RBI or other financial sector regulators, to the extent permissible under the applicable regulatory prescriptions.
2.8 Systemically important non-deposit taking non-banking financial company
Non-banking financial company not accepting/holding public deposits and having total assets of ` 500 crore and above as shown in the last audited balance sheet.
3. Benefits of incorporating NBFC
-
- Competitive Interest Rates: Rate of interest is one of the main aspects of all types of loans. Non-Banking Financial Sectors have started to concentrate on this area in the recent decades and have brought down the interest rates to either equal to bank lending rates or at times even lower to bank rates.
- Quick Processing: The applicant should fulfil the eligibility criteria but NBFC are lenient in this aspect. This makes loan approval process easier, smoother and quicker.
Less - Rules and Regulations: NBFC are incorporated under the Companies Act, (though regulated by the Reserve Bank of India), the rules and regulations for lending are not as stringent as banks. This helps borrowers to get loans easily. In view of less complicated loan processing requirements, borrowers are highly satisfied.
- Loan available for Individuals with Poor Credit Rating: Individuals with poor credit rating generally will not get loans from banks. The reason for this is banks consider borrowers are high-risk individuals if the credit scoring is low.
4. Incorporation of NBFCs and registration process with RBI
-
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are companies incorporated under Companies Act, 2013.
- The procedure for incorporating a Non-Banking Finance Company (NBFC) is the same as any other company.
- Form Spice + for approval of name should contain financing as the principal activity.
- Their principal business to be stated in the MOA while registering under the Companies Act shall be lending credit, making investments in various types of shares and stocks, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance business, chit business, and receiving deposits under any scheme or arrangement.
- Net Owned Funds of the entity should be not less than Rupees Two Crore and the Authorised Share Capital of the NBFC is not less than Rupees Two Crore.
5. Registration process with Reserve Bank of India
Stage 1: Before applying for registration, the company should ensure the following:
-
- It should have minimum one director from NBFC background or senior Bankers as full-time director in the company.
- Clean CIBIL records.
- Understanding of NBFC/Finance business.
Stage 2: Non-banking Financial company can commence or carry on business of a non-banking financial institution only after:
-
- obtaining a certificate of registration from the Reserve Bank of India and
- having a Net Owned Funds of Rupees Two Crore.
Stage 3: To obviate dual regulation, certain categories of NBFCs which are regulated by other regulators are exempted from the requirement of registration with RBI:
-
- Venture Capital Fund/Merchant Banking companies/Stock broking companies registered with SEBI.
- Insurance Company holding a valid Certificate of Registration issued by IRDA
- Nidhi companies as notified under the Companies Act,1956/2013.
- Chit companies as defined in clause (b) of Section 2 of the Chit Funds Act, 1982.
- Housing Finance Companies regulated by National Housing Bank.
- Stock Exchange or a Mutual Benefit company.
6. Procedure for filing application with Reserve Bank of India
Step 1: The applicant company is required to apply online and submit a physical copy of the application along with the necessary documents to the Regional Office of the Reserve Bank of India.
Step 2: The application can be submitted online by accessing RBI’s secured website https://cosmos.rbi.org.in. At this stage, the applicant company will not need to log on to the COSMOS application and hence user ids are not required.
Step 3: The company can click on “CLICK” for Company Registration on the login page of the COSMOS Application. A window showing the Excel application form available for download would be displayed. The company can then download suitable application form (i.e. NBFC or SC/RC) from the above website, key in the data and upload the application form.
Step 4: The company may note to indicate the correct name of the Regional Office in the field “C-8” of the “Annex- Identification Particulars” in the Excel application form. The company would then get a Company Application Reference Number (CARN) for the CoR application filed online.
Step 5: The company has to submit the hard copy of the application form (indicating the online Company Application Reference Number) along with the supporting documents to the concerned Regional Office.
Step 6: The company can then check the status of the application from the above mentioned secure address by keying in the acknowledgement number.
7. Housing Finance Companies
7.1 Meaning
-
- Housing Finance Company (HFC) is a type of non-banking financial institution which is primarily engaged in the business of providing home loans and other related products. Unlike other Non-Banking Financial Companies which are governed under the regulatory framework of RBI, HFCs are regulated by the National Housing Bank (NHB).
- No Housing Finance Company shall commence or carry on the business of a housing finance institution without:
1. Obtaining a certificate of registration from National Housing Bank issued under Chapter V of the said Act, and
2. Having the net owned fund of Rupees 10 Crore or such other higher amount, as the National Housing Bank may by notification, specify.
7.2 Registration of Housing Finance Company
-
- Form Spice + for approval of name should contain housing financing as the principal activity.
- Their principal business to be stated in the MOA, while registering under the Companies Act shall be providing finance for housing and related matters.
- Net Owned Funds of the entity should be not less than Rupees Ten Crore, it is advisable that the Authorised Share Capital of the HFC is not less than Rupees Ten Crore.
- A company registered under the Companies Act and desirous of commencing business of a housing finance institution should comply with the following:
1. either it should primarily transacts or has as one of its principal objects of transacting the business of providing finance for housing, whether directly or indirectly;
2. it should have a minimum net owned fund of Rupees 10 crore.
-
- NHB after satisfying itself on the fulfilment of following conditions provided under Section 29A(4) of the National Housing Bank Act, 1987 may grant a Certificate of Registration:
1. HFC is or shall be in a position to pay its present or future depositors in full as and when their claims accrue;
2. Affairs of the HFC are not being or are not likely to be conducted in a manner detrimental to the interest of its present or future depositors;
3. HFC has adequate capital structure and earning prospects;
4. Public interest shall be served by the grant of certificate of registration to the HFC to commence or carry on the business in India;
5. Grant of certificate of registration shall not be prejudicial to the operation and growth of the housing finance sector of the country;
6. Any other condition, fulfilment of which in the opinion of the NHB, shall be necessary to ensure that the commencement of or carrying on the business in India by a HFC shall not be prejudicial to the public interest or in the interests of the depositors.
-
- HFCs are categorized in terms of the type of liabilities, by NHB into Deposit and Non-Deposit accepting HFCs and are issued Certificate of Registration.
8. Asset Reconstruction Company (ARC)
Asset Reconstruction Company (Securitization Company/Reconstruction Company) is a company registered under Section 3 of the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
8.1 Functions performed by ARC
-
- Acquisition of financial assets.
- Change or takeover of Management/Sale or Lease of Business of the Borrower.
- Rescheduling of Debt.
- Enforcement of Security Interest.
- Settlement of dues payable by the borrower.
8.2 Benefits of Incorporating an ARC
-
- ARCs also helps building industry expertise in loan resolution and restructuring management besides serving as a catalyst for important legal reforms in bankruptcy procedures and loan collection.
- ARCs play an important role in developing capital markets through secondary asset instruments.
- Transfer should help restore depositor and investor confidence by ensuring the lender’s financial health. The banks use it as a method to hive off the bad loans from their balance sheet. ARCs can maximise recovery value while minimizing costs.
- Relieving banks of the burden of NPAs will allow them to focus better on managing the core business including providing new business opportunities for the ARC.
8.3 Asset Reconstruction Company – the Registration Process
-
- A company has to be incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013. The company may be a private company or a public company.
- Secondly, after incorporation, the company has to register itself with the Reserve Bank of India.
9. Micro Finance Institutions (MFI)
-
- Micro finance institution is an organization that offers financial services to low income populations.
- An increasing number of microfinance institutions (MFIs) are seeking non-banking finance company (NBFC) status from RBI to get wide access to funding including bank finance.
9.1 Characteristics of MFIs
-
- Size of the loan given by the MFI is small.
- Repayment period is short.
- MFI can mobilise resources both from internal and external sources.
- No collateral for loan is required.
- Purpose of end use of loan is flexible.
- Loans given are mostly group loans trickling down to individuals.
- Transaction cost is low due to group lending.
9.2 Incorporation of MFI
-
- Firstly, a company has to be incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013. The company may be a private company or a public company.
- Secondly, after incorporation the company has to register itself with the Reserve Bank of India since Micro Finance Institution is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
9.3 List of documents to be filed with RBI for registration
-
- Certified copies of Certificate of Incorporation.
- Certified copies of extract of only the main object clause in the MOA relating to the financial business.
- Board resolution stating that:
1. company is not carrying on any NBFC activity/stopped NBFC activity and will not carry on/commence the same before getting registration from RBI.
2. company has not accepted any public deposit, in the past (specify period)/does not hold any public deposit as on the date and will not accept the same in future without the prior approval of Reserve Bank of India.
3. company has formulated “Fair Practices Code” as per RBI Guidelines.
-
- Copy of Fixed Deposit receipt & bankers certificate of no lien indicating balances in support of NOF.
- For companies already in existence, the Audited balance sheet and Profit & Loss account along with directors & auditors’ report or for the entire period the company is in existence or for last three years whichever is less should be submitted.
- Copy of the certificate of highest educational and professional qualification in respect of all the directors.
- Copy of experience certificate (if any) in the Financial Services Sector (including Banking Sector) in respect of all the directors.
- Bankers’ report in respect of applicant company its group/subsidiary/associate/holding company/related parties, directors of the applicant company having substantial interest in other companies.
10. Nidhi Companies
-
- Nidhi Company is one that belongs to non-banking finance sector and is recognized under section 406 of the Companies Act, 2013.Their core business is borrowing and lending money between their members.
- Regulated by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India and are registered under the Companies Act, 2013 read with Nidhi Rules, 2014.
10.1 Characteristics of Nidhi Company
-
- It is allowed to transact business only with its members and with nobody else. In case a person wishes to place deposit with a Nidhi or borrow money from a Nidhi, he/she must first become a member (shareholder) of the Nidhi by subscribing to equity shares.
- After commencement of the Companies Act, 2013, no Nidhi shall issue preference shares.
- They are allowed to open branches subject to compliance with Rule 10 of the Nidhi Rules, 2014, but do not operate on a pan India basis.
- They are incorporated as public companies with a minimum paid up equity share capital of ` 5,00,000.
- Loans may be provided only to its members and should be fully secured.
- Director of a Nidhi shall be a member and shall hold office for a term upto 10 consecutive years on the Board of a Nidhi.
- Nidhi can declare dividend not exceeding 25% and any higher amount shall be specifically approved by the Regional Director.
- Nidhi shall adhere to the prudential norms for revenue recognition and classification of assets in respect of mortgage loans or jewel loans as provided in Rule 20 of the Nidhi Rules, 2014.
10.2 General restrictions or prohibitions on Nidhis (Rule 6)
-
- No Nidhi shall:
1. carry on the business of chit fund, hire purchase finance, leasing finance, insurance or acquisition of securities issued by any body corporate.
2. issue preference shares, debentures or any other debt instrument by any name or in any form whatsoever.
3. open any current account with its members.
4. accept deposits from or lend to any person, other than its members.
5. pledge any of the assets lodged by its members as security.
6. take deposits from or lend money to any body corporate.
7. enter into any partnership arrangement in its borrowing or lending activities.
8. issue or cause to be issued any advertisement in any form for soliciting deposit. Private circulation of the details of fixed deposit Schemes among the members of the Nidhi carrying the words “for private circulation to members only” shall not be considered to be an advertisement for soliciting deposits.
9. pay any brokerage or incentive for mobilising deposits from members or for deployment of funds or for granting loans.
10. carry on any business other than the business of borrowing or lending in its own name. Nidhis which have adhered to all the provisions of these rules may provide locker facilities on rent to its members subject to the rental income from such facilities not exceeding 20% of gross income of the Nidhi at any point of time during a financial year.
11. raise loans from banks or financial institutions or any other source for the purpose of advancing loans to members of Nidhi.
12. acquire or purchase securities of any other company or control the composition of the Board of Directors of any other company in any manner whatsoever or enter into any arrangement for the change of its management.
10.3 Benefits of Incorporating Nidhi Company
-
- Nidhi mobilises small savings, mostly of the middle class and disburses loans to eligible borrowers. Owing to their small size and closeness to the customers, disbursement of loans is speedy. This is especially useful in case the borrower is in urgent needs of funds.
- Repayment is guaranteed as the loans are secured and due to peer pressure, borrowers ensure that loan is repaid on due dates.
- Nidhis offer a higher rate of interest on deposits. This makes it an attractive investment opportunity for people especially the senior citizens.
- BODs of Nidhi consists of senior persons who have experience in handling finances, who are well respected in social circles resulting in credibility to the institution and build confidence in the minds of borrowers and depositors.
10.4 Incorporation of a Nidhi Company
-
- The normal procedure for incorporating a public company is required to be complied with such as obtaining availability of name, filing of Memorandum and Articles of Association and other related documents.
- Care must be taken to see that the Objects Clause of the Memorandum should restrict itself to the object of cultivating the habit of thrift and savings amongst its members, receiving deposits from and lending to its members only for their mutual benefit and for other permitted purposes.
- The name of the company should end with the words “Nidhi Limited”.
- As per Rule 5 of the Nidhi Rules, 2014, every Nidhi shall within a period of 1 year from date of its incorporation ensure that it has –
1. Not less than two hundred members;
2. Net Owned Funds of ten lakh rupees or more;
3. Unencumbered term deposits of not less than ten per cent of the outstanding deposits;
4. Ratio of Net Owned Funds to deposits of not more than 1:20.
5. The provisions of Rule 5 of the Nidhi Rules, 2014 shall not be applicable for the companies incorporation as Nidhi on or after the commencement of Nidhi (Amendment) Rules, 2022 i.e. 19th April, 2022.
10.5 MCA Advisory on Sensitization of Nidhi Companies
Time-frame for applying to Central Government in form NDH-4 is as under:
-
- Companies incorporated as Nidhi before Nidhi Amendment Rules, 2019 i.e. 15.08.2019: Apply within period of one year from the date of its incorporation or within 9 months of the Nidhi Amendment, Rules i.e. 15.08.2019 whichever is later.
- Companies incorporated as Nidhi on or after Nidhi Amendment Rules, 2019 i.e. 15.08.2019: Apply within 60 days of expiry of one year from the date of incorporation or extended period (as granted by concerned Regional Director).
1. In case a company does not comply with the above requirements, it shall not be allowed to file Form No. SH–7 (Notice to Registrar for any alteration of share capital) and Form PAS–3 (Return of Allotment).
2. Such companies are required to ensure strict adherence to provision of Companies Act, 2013 and Nidhi Rules, 2014 as amended.
3. Investors are advised to verify the status of Nidhi Company from the notification issued by Central Government in official gazette before making any investment or deposit.
11. Payment Banks
11.1 Meaning of Payment Banks
-
- Payments Banks is a new model of banks conceptualised by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Payments banks can issue services like ATM cards, debit cards, net-banking, third party transfers and mobile-banking and offer remittance services. These banks cannot grant loans or issue credit cards.
- Main objective of payments bank is to widen the spread of payment and financial services to small business, low-income households and migrant labour workforce in secured technology-driven environment.
- To open a bank account and the application process of payments bank is made very easy as compared to other banks. These bank accounts can be opened instantly through their respective mobile apps just by providing details like Aadhaar number with KYC verification.
11.2 Regulations
Key issues which requires compliance by an applicant company are:
-
- Minimum capital requirement is INR 100 crore.
- For the first five years, the stake of the promoter should remain at least 40%.
- Foreign share holding will be allowed in these banks as per the rules for FDI in private banks in India.
- Voting right of any shareholder is capped at 10%, which can be raised to 26% by Reserve Bank of India. Any acquisition of more than 5% will require approval of the RBI.
- Majority of the bank’s board of directors should consist of independent directors appointed according to RBI guidelines.
- Bank should be fully networked from the beginning. It cannot form subsidiaries to undertake non-banking activities.
- Deposits will be capped at INR 1,00,000 per customer but it may be raised by the RBI based on the performance of the bank.
- Bank cannot undertake lending activities. 25% of its branches must be in the unbanked rural area.
- Bank must use the term “payments bank” in its name to differentiate it from other types of bank.
- Banks will be licensed as payments banks under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Registered as Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 2013.
Also Read:
What are the functions of RBI under FEMA?
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied



 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
