Compounding of Contravention under FEMA
- Blog|FEMA & Banking|
- 11 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 5 February, 2024

Niki Shah – Partner | SN & Co.
Table of Contents
- What is Compounding?
- When should one apply for Compounding?
- What are Compounding Orders?
- Total Compounding order passed by RBI
- Statistical Facts
- Provisions
- Powers to Compound
- Delegation of Powers to Regional Offices/Sub-Offices
- Contraventions Compounded by FED CO Cell, New Delhi
- Contravention of Provisions under FEMA, 1999
- Benefits of Compounding
- Pre-requisite for Compounding Process
- Compounding Process
- Computation of Penalty
- Penalty to Compounding
- Late Submission Fees (LSF)
- Documentation Requirement
- Compounding Orders
1. What is Compounding?
- Compounding is the admission of a violation of any of the provisions of the FEMA Act of 1999
- It refers to admitting a Contravention, pleading guilty and seeking remedy.
- Or violation of the rules/regulations/notifications/orders/directions, or circulars issued under the Act
- The provisions of section 15 of FEMA, 1999 permit compounding of contravention
- The offence must be compounded within 180 days of the date of receipt of the application.
2. When should one apply for Compounding?
- When a person is made aware of the contravention of the provisions of FEMA, 1999 by
- the Reserve Bank or
- any other statutory authority or
- the auditors or
- by any other means, she/he may apply for compounding.
- One can also make an application for compounding, suo moto, on becoming
aware of the contravention.
3. What are Compounding Orders?
- Vide A.P. (Dir Series) Circular No. 73 dated 26/05/2016, RBI decided to opt for public disclosure of compounding orders.
- Till date, 4540 orders have been hosted on the RBI website.
- Compounding orders are concise, outlining facts, emphasizing the violated provision, and specifying the compounding fee.
- Does not hold any precedence value and only immense guidance value.
- Analyzing compounding orders offers key insights into the RBI’s application of FEMA provisions and relevant notifications, providing valuable interpretive principles.
4. Total Compounding order passed by RBI
| Amount imposed under Compounding (in INR) |
No. of Cases |
% |
| Rs. 1 – Rs. 1 Lacs |
2623 |
58% |
| Rs. 1 Lacs – Rs. 10 Lacs |
1486 |
33% |
| Rs. 10 Lacs – Rs. 1 Cr |
374 |
8% |
| Rs. 1 Cr and above |
57 |
1% |
| Total |
4540 |
100% |
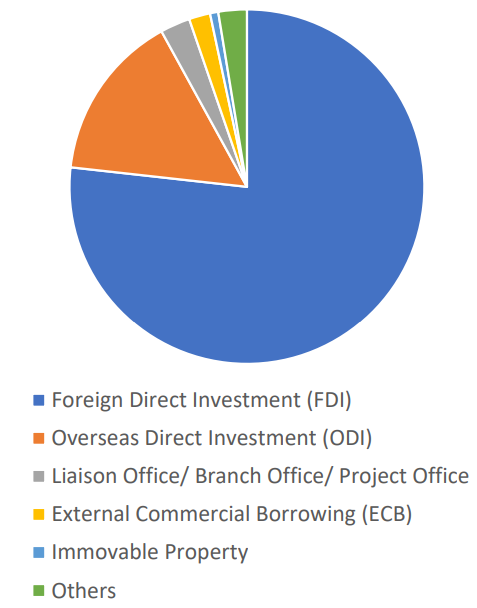
5. Statistical Facts
| Areas |
No. of Cases |
% |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
1747 |
77% |
| Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) |
347 |
15% |
| Liaison Office/Branch Office/Project Office |
62 |
3% |
| External Commercial Borrowing (ECB) |
44 |
2% |
| Immovable Property |
17 |
1% |
| Others |
59 |
3% |
| Total |
2,276 |
100% |
6. Provisions
Regulatory Provisions:
- Section 15 of the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 read with Section 13
Governing Provisions:
- Foreign Exchange Management (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2000, as amended
- Master Direction on Compounding of Contraventions under FEMA, 1999 – No.04/2015-16 dated January 1, 2016, as amended
7. Powers to Compound
| Contravention of Section 3(a) of FEMA,1999 | Any Other Contravention |
| Deputy Direction of DoE – Amount involved less than Rs. 5 lacs | Assistant General Manager of RBI – Rs. 10 Lacs or below |
| Additional Director of DoE – Rs. 5 lacs upto Rs. 10 Lacs | Deputy General Manager of RBI – Rs. 10 lacs – Rs. 40Lacs |
| Special Director of DoE – Rs. 10 Lacs upto Rs. 50 Lacs | General Manager of RBI – Rs. 40 lacs – Rs. 1 Crore |
| Special Director with Deputy Legal Adviser of DoE – Rs. 50 Lacs upto Rs.1 Crore | Chief General Manager of RBI – Rs. 1 Crore and above |
| Director of Enforcement with Special Director of DoE – Above Rs. 1 Crore |
No Contravention shall be compounded unless the amount involved in such contravention is quantifiable.
Section 3(a) of FEMA, 1999 – deal in or transfer any foreign exchange or foreign security to any person not being an authorised person;
8. Delegation of Powers to Regional Offices/Sub-Offices
FEMA 20/2000-RB dated May 3, 2000
- Paragraph 9(1)(A) of Schedule 1
- Paragraph 9(1)(B) of Schedule 1
- Paragraph 9(2) of Schedule 1
- Paragraph 8 of Schedule 1
- Paragraph 5 of Schedule 1
- Regulation 2(ii) read with Regulation 5(1)
- Paragraph 2 or 3 of Schedule 1 (Issue of shares without approval of RBI or Government, wherever required)
- Regulation 10A (b)(i) read with paragraph 10 of Schedule 1
- Regulation 10B (2) read with paragraph 10 of Schedule 1
- Regulation 4 (Receiving investment in India from non-resident or taking on record transfer of shares by investee company)
- Regulation 14(6)(ii)(a)
- Paragraphs 7(1) (for the period upto 02.03.2017) and 6(1) (for the period 03.03.2017 to 06.11.2017) of Schedule 9
- Regulation 10(A)(a)
FEMA 20(R)/ 2017-RB dated November 07, 2017
- Regulation 13.1(1)
- Regulation 13.1(2)
- Regulation 13.1(3)
- Paragraph 2 of Schedule 1
- Regulation 11
- Regulation 2(v) read with Regulation 5
- Regulation 16.B (Issue of shares without approval of RBI or Government, wherever required)
- Regulation 13.1(4)
- Regulation 4 (Receiving investment in India from non-resident or taking on record transfer of shares by investee company)
- Regulation 13.1(11)
- Regulations 13.1(7) and 13.1(8)
- Regulation 10(5)
|
FEM (Non –Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019 dated October 17, 2019 |
|
| Rule 2(k) read with Rule 5 | Definition of equity instruments |
| Rule 21 | Pricing Guidelines |
| Paragraph 3 (b) of Schedule I (Issue of shares without approval of RBI or Government, wherever required) | Sectoral Caps for total foreign investment |
| Rule 4 (Receiving investment in India from non-resident or taking on record transfer of shares by Investee Company) | Restriction on receiving investment |
| Rule 9(4) and Rule 13(3) | Transfer of equity instruments by NRI or OCI |
|
FEM (Mode of Payment and Reporting of Non-Debt Instruments) Regulations dated October 17, 2019 (FEMA 395/2019-RB) |
|
| Regulation 3.1(I)(A) | Mode of Payment |
| Regulation 4(1) | Form FC-GPR |
| Regulation 4(2) | Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) |
| Regulation 4(3) | Form FC-TRS |
| Regulation 4(6) | Form LLP(I) |
9. Contraventions Compounded by FED CO Cell, New Delhi
- The officers attached to the FED, CO, Cell at New Delhi office are authorized to compound the contraventions as per details below:
|
FEMA Notifications |
|
| FEMA 7/2000-RB, dated 3-5-2000/FEMA 7(R)/2015-RB dated 21-1-2016 | Acquisition and transfer of immovable property outside India |
| FEMA 21/2000-RB, dated 3-5-2000/FEMA 21(R)/2018- RB, dated 26-3-2018/Chapter IX of Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019 dated 17-10-2019 | Acquisition and transfer of immovable property in India |
| FEMA 22/2000-RB, dated 3-5-2000/FEMA 22(R)/2016-RB dated 31-3-2016 | Establishment in India of branch or office or other place of business |
| FEMA 5/2000-RB, dated 3-5-2000/FEMA 5(R)/2016-RB dated 1-4-16 | Deposit Regulations |
- Amounts Above 1 Crore – Regional Office at Panaji and Kochi will have no jurisdiction. Mumbai Regional Officer and Thiruvananthapuram Regional Office would compound such contraventions.
10. Contravention of Provisions under FEMA, 1999
ODI
- Non submission of form ODI after investment & UIN not allotted
- Not a permitted method of Funding
- Not obtaining Share certificate within stipulated time period from the date of Remittance
- Non Submission of Annual Performance Reports (APR) every year
ECB
- Not an eligible borrower
- Lender not a recognized lender
- Minimum Maturity period not adhere to
- Breach of all in cost ceiling
- End use not a permitted one
- LRN not obtained
FDI
- Non reporting of Inward remittance within 30 days
- Not allotting equity instrument or refunding the amount within 180 days
- Not submitting Form FCGPR within 30 days from the date of allotment
- Non Submission of Form FCTRS on transfer of shares
- Issue of instrument other than equity shares, fully or CCPS as prescribed
Sensitive Contraventions
- Cases involving serious contravention suspected of money laundering, terror financing or affecting sovereignty and integrity of the nation are categorized as sensitive contraventions.
11. Benefits of Compounding
- It is a voluntary process
- Comforts of citizens and corporate community
- Personal hearing is not mandatory
- Minimizing transaction costs
- Time-bound disposal (180 Days)
- Changing dynamics of our economy
- Simple and hassle-free procedure
- No proceeding or further proceedings initiated or continued
- Absolutely transparent
- It saves time and energy One application – One hearing – One order for one notification.
12. Pre-requisite for Compounding Process
- The company must not make similar contraventions within a 3 year period of compounding.
- Compoundable contraventions requiring approvals from any authorities must obtain necessary permissions before applying for compounding.
- Any suspected serious contraventions such as money laundering, terror financing, or compromising national sovereignty trigger referral to the Directorate of Enforcement for further investigation if the contravener fails to pay the compounding penalty within the stipulated period.
- Contraventions that have undergone adjudication by the Directorate of Enforcement and are under appeal according to sections 17 or 19 of FEMA, 1999, are non compoundable.
13. Compounding Process
- Submission of application to RBI and not AD bank in the prescribed format.
- Payment of fees – of Rs. 5,000/- by way of DD in favour of RBI
- Examination by RBI
- Calling for additional documents, if required
- Opportunity for personal hearing
- Passing compounding order
- Payment of penalty
- Issuance of certificate of payment of a penalty
- Separate formats are provided in Annex II for FDI, ECB, ODI & Branch Office/Liaison Office
- Format for FDI
-
- Name of the applicant, Date of incorporation, Income-tax PAN, Nature of activities undertaken (Please give NIC code – 1987/2008), Brief particulars about the foreign investor
- Details of foreign inward remittances received by Applicant Company from date of incorporation till date
Table A
|
SI. No. |
Name of Remitter | Total Amount (INR) | Date of Receipt | Reported to RBI on* |
Delay if any |
| Total |
* date of reporting to RBI and not AD
Table B
|
Name of Investor |
Date of allotment of shares | Number of shares allotted | Amount for which shares allotted | Date of reporting to RBI |
Delay if any |
| Total |
*date of reporting to RBI and notAD
Table C
|
SI. No. |
Name of Remitter | Total Amount (INR) | Date of Receipt | Excess share application Money | Date of refund of share application Money | Amount in forex |
RBI approval letter and date |
| Total |
*date of reporting to RBI and not AD
Table D
|
Authorized Capital |
|||||
| SI. No. | Date | Authorized Capital | With effect from | Date of Board Meeting |
Date of filing with ROC |
A=B+C
14. Computation of Penalty
As per provisions of section 13 of FEMA the amount imposed can be up to three times the amount involved in the contravention. However, the amount imposed is calculated based on guidance note given below.
| Type of contravention | Existing Formula |
| 1] Reporting Contraventions
A) FEMA 20 Para 9(1)(A), 9(1)(B), part B of FC(GPR), FCTRS (Reg. 10) and taking on record FCTRS (Reg. 4) B) FEMA 3 Non submission of ECB statements C) FEMA 120 Non reporting/delay in reporting of acquisition/setup of subsidiaries/step down subsidiaries /changes in the shareholding pattern D) Any other reporting contraventions (except those in Row 2 below) E) Reporting contraventions by LO/BO/PO |
Fixed amount: Rs10000/- (applied once for each contravention in a compounding application) +
Variable amount as under: As above, subject to ceiling of Rs.2 lakhs. In case of Project Office, the amount imposed shall be calculated on 10% of total project cost. |
| 2] AAC/ APR/ FLAR/ Share certificate delays
In case of non-submission/delayed submission of APR/share certificates (FEMA 120) or AAC (FEMA 22) or FCGPR (B) or FLA Returns – FEMA 20/FEMA 20 (R)/FEMA 120/FEMA 395 |
Rs. 10000/- per AAC/APR/FCGPR (B)/FLA Return delayed.
Delayed receipt of share certificate – Rs. 10000/- per year, the total amount being subject to ceiling of 300% of the amount invested. |
| 3]
A] Allotment/Refunds Para 8 of FEMA 20/2000-RB (non-allotment of shares or allotment/refund after the stipulated 180 days) B] LO/BO/PO (Other than reporting contraventions) |
Rs. 30000/- + given percentage:
1st year: 0.30% 1-2 years: 0.35% 2-3 years: 0.40% 3-4 years: 0.45% 4-5 years: 0.50% >5 years: 0.75% (For project offices the amount of contravention shall be deemed to be 10% of the cost of project) |
| 4] All other contraventions, –including all contraventions of FEMA20(R)/2017/NDIR, 2019/FEMA 395/ 2019/, except contraventions pertaining to FLA returns and corporate guarantees | Rs. 50000/- + given percentage:
1st year: 0.50% 1-2 years: 0.55% 2-3 years: 0.60% 3-4 years: 0.65% 4-5 years: 0.70% >5 years: 0.75% |
| 5] Issue of Corporate Guarantees without UIN/without permission wherever required/open ended guarantees or any other contravention related to issue of Corporate Guarantees. |
Rs. 500000/- + given percentage:
1st year: 0.050% 1-2 years: 0.055% |
|
*The contraventions of FEMA 20 existing and continuing as on November 07, 2017 (i.e. the starting date of contraventions prior to November 07, 2017) will be compounded as per 1(A) above.A |
|
Additional Provisions
- The amount imposed should not exceed 300% of the amount of contravention
- In case the amount of contravention is less than Rs. One lakh, the total amount imposed should not be more than amount of simple interest @5% p.a. calculated on the amount of contravention.
- In case of Transfer or issue of security by a person resident outside India, the amount imposed will be further graded as under:
| Shares Allotted | Times of amount calculated |
| After 180 Days without prior approval | 1.25 Times |
| Not allotted and amount refunded after 180 days with permission | 1.50 Times |
| Not allotted and amount refunded after 180 days without permission | 1.75 Times |
- In cases where it is established that the contravener has made undue gains, the amount thereof may be neutralized to a reasonable extent by adding the same to the compounding amount calculated as per
- If a party who has been compounded earlier applies for compounding again for similar contravention, the amount calculated as above may be enhanced by 50%.
15. Penalty to Compounding
- The amount should be paid within 15 days from the date of the order by way of a demand draft drawn on “Reserve Bank of India” and payable at the Regional office/Sub-office/Central Office Cell, New Delhi which has issued the compounding order and at Mumbai if the order is issued by CEFA, Central Office, Mumbai
- Appeal against the order of the Compounding Authority?
There is no provision under the of FE (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2000, for an appeal against the order of the Compounding Authority or for a request for reduction of amount imposed or extension of period for payment of the amount imposed.
16. Late Submission Fees (LSF)
- The Late Submission Fee (LSF) was introduced for reporting delays in Foreign Investment (FI), External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) and Overseas Investment related transactions with effect from November 07, 2017, January 16, 2019 and August 22, 2022 respectively. It has now been decided to bring uniformity in imposition of LSF across functions. The following matrix shall be used henceforth for calculation of LSF, wherever
applicable:
| Sr. No. | Type of Reporting delays | LSF Amount (INR) |
| 1 | Form ODI Part-II/ APR, FCGPR (B), FLA Returns, Form OPI, evidence of investment or any other return which does not capture flows or any other periodical reporting | 7500 |
| 2 | FC-GPR, FCTRS, Form ESOP, Form LLP(I), Form LLP(II), Form CN, Form DI, Form InVi, Form ODI-Part I, Form ODI-Part III, Form FC, Form ECB, Form ECB-2, Revised Form ECB or any other return which captures flows or returns which capture reporting of non-fund transactions or any other transactional reporting | [7500 + (0.025% × A × n)] |
- Time Frame: LSF option can be availed till a period of three years from the due date of reporting or submission. Post expiry of the said three years, the contravener will continue to have the ability to apply for compounding procedure as established under FEMA for rectifying the delays in filings.
- The new matrix for calculation of LSF may prove either beneficial or detrimental for a contravener, when compared with the old regime, based on variables such as the amount and the time involved (examples)
| Contravention | Compounding | LSF |
| Delayed Filing Minimum
Maximum |
Rs. 100 (Foreign Investment) or Rs. 5000 (ECB)
300% of the amount involved |
Rs. 7,500
100% of amount involved |
| Delayed filing of Form ECB-2 for a year (borrowing Rs. 100 Crs) | Rs. 50,000 | Rs. 2,57,500 |
Major Differences
| Compounding | Late Submission Fees (LSF) |
| Purpose: Compounding is a process by which contraventions of FEMA provisions can be regularized or condoned by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). | Purpose: Late submission fees are imposed for delays in submitting required documents or information under FEMA. |
| Completion of proceedings: within 180 Days | Completion of proceedings: Immediate |
| Maximum Penalty: 300% of Amount Involved | Maximum Penalty: 100% of Amount Involved |
| Payment within 15 Days of order | Payment within 30 Days from the issuance of LSF payment advice. |
| In case of non payment within 15 days such case shall be referred to DoE | In case of non payment within 30 days such case shall be considered null and void and any LSF received beyond this period shall not be accepted. |
17. Documentation Requirement
- Compounding application in the format prescribed by RBI From time to time
- Along, with the prescribed fee of Rs. 5000/- by way of a demand draft drawn in favour of “Reserve Bank of India”
- Additional details as per the Annexes- relating to Foreign Direct Investment, External Commercial Borrowings, Overseas Direct Investment and Branch Office/Liaison Office, as applicable
- An undertaking that they are not under investigation of any agency such as DoE, CBI, etc- (No Format specified)
- Duly filled ECS mandate form
- A copy of MoA and latest Audited BS while applying
- Application must contain contact details, name of the applicant, Mobile no.,
and email Id
18. Compounding Orders
Factors Taken Into Account While Passing Compounding Order
- Amount of gain/unfair advantage received as a result of contravention (wherever quantifiable)
- Amount of loss caused to authority/agency/exchequer due to contravention
- Economic benefit to the contravener due to delayed nature of compliance or avoiding such compliance
- Repetitive nature of contravention. Track record/History of non compliance
- Contravener’s conduct – while undertaking the transaction/disclosure of full facts in Application. Submission made during personal hearing.
- Any other factor considered relevant/appropriate.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied





 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
