Overview of the National Income Accounting and Related Concepts
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 11 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 30 January, 2024

Table of contents
- Introduction
- Methods of Measuring National Income
- Value added Method Or Product Method
- Income Method
- Expenditure Method
- Measurement of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Market Prices
- Measurement of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Factor Cost
- Net Domestic Product (NDP)
- Nominal and Real GDP
- GDP Deflator
- Measurement of Gross National Product (GNP) At Market Prices
- Measurement of Gross National Product (GNP) at Factor Cost
- Computation of Net National Product (NNP)
- Domestic Income
- Types of Income – Private, Personal, Disposable, Real and Per-Capita income
Check out Taxmann's Economic & Business Environment (Paper 3) | CRACKER which covers all past exam questions (topic-wise) & detailed answers for the CSEET exam by ICSI. It also covers memory-based and important past exam questions and questions from CSEET e-Bulletin and MTPs of ICSI. CSEET | New Syllabus | May 2024 Exam
1. Introduction
- National Income is a concept of Macro-Economics.
- It is always expressed in terms of money.
- In common parlance, national income means the total value of goods and services produced annually in a country.
- In other words, the total amount of income accruing to a country from economic activities in a year’s time is known as national income. It includes payments made to all resources in the form of wages, interest, rent and profits.
- National Income is calculated as NNP at FC.
- The National Income includes Net Factor Income Earned from Abroad also.
2. Methods of Measuring National Income
The following are the methods of measuring the national income of a country.
- The Product Method or Value-Added Method.
- The Income Method.
- The Expenditure Method
The three methods give the same value of national income
3. Value added Method Or Product Method
3.1 Concept of Value-Added Method
- The Product method measures the contribution of each producing enterprise in the domestic territory of the country.
- Every individual enterprise adds certain value to the products, which it purchases from some other firm as intermediate goods. The national income is the summation of value addition by each and every individual firm.
- Value Added = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption
- This approach involves adding up the value of all the final goods and services produced in the country during the year. The main sectors whose production value is added up are:
-
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Transport and communication
- Banking
- Administration and defence and
- Distribution of income.
3.2 Steps in Value Added Method
| (1) Identification and classification of production units | The producing enterprises are identified and classified into individual sectors according to their activities. |
| (2) To estimate Gross domestic Product at Market Price [GDPMP] | GDPMP = Sum total of GVAMP of all sectors i.e.,åGVAMP |
| (3) To calculate Domestic Income i.e. NDPFC | NDPFC = GDPMP – Depreciation – Net Indirect Taxes |
| (4) To estimate National Income (NNPFC) | NNPFC=NDPFC+ Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) |
3.3 Precautions for Value Added Method
- Items Not Included: The following are NOT included in the national Income:
-
- Intermediate goods
- Sale and purchase of second-hand goods
- Production of goods and services for self-consumption
- Items should be Included: The following should be included in the national Income:
-
- Imputed value of owner-occupied houses
- Change in stock of goods (inventories)
- Problem of Double Counting: In measuring the national income, the value of only final goods and services is to be included. The problem of double counting arises when value of intermediate goods is also included along with value of final goods. There are two alternative ways to avoid double counting:
-
- Final Output method i.e. to include value of final goods only.
- Value added method i.e. to include sum total of the value added by each producing unit.
4. Income Method
4.1 Concept of Income Method
- This method measures National Income from the perspective of factor incomes.
- As per this method, the National Income is the summation of all the incomes that accrue in the factors of production by way of wages, profits, rent, interest., etc.
- The sum total of all the factor incomes earned within the domestic territory of a country is known as Domestic Income [NDPFC]
- The following are the components of factor income:
-
- Wages and salaries in cash (all monetary benefits), non-monetary benefits (like rent free accommodation, free medical, free car, etc.) and employer’s contribution to social security schemes (like provident fund, gratuity, etc.).
- Rent and Royalty, which arises from ownership of land and building.
- Interest, which is received by lending funds to a production unit.
- Profit, which is the reward to the entrepreneur for his contribution to the production of goods and services.
- Mixed Income, which is generated by own-account workers and unincorporated enterprises.
4.2 Steps of Income Method
| (1) Identification and classification of production units | The producing enterprises, employing various factors of production, are identified and classified into primary, secondary and tertiary sectors. |
| (2) To estimate the factor income paid by each sector | The factor incomes paid by each sector are classified under the following heads:
(i) compensation of Employees |
| (3) To calculate Domestic Income i.e. NDPFC | NDPFC = compensation of Employees + Rent and Royalty + interest + Profit + Mixed Income |
| (4) To estimate National Income (NNPFC) | NNPFC =NDPFC+ Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) |
4.3 Precautions for Income Method
- Items Not Included: The following are NOT included in the national Income:
-
- Transfer Incomes like gifts, donation, charity, scholarship, etc.
- Illegal money earned through smuggling and gambling
- Windfall gains such as prizes won, lotteries etc.
- Receipts from the sale of financial assets such as shares, bonds.
- Income from sale of second-hand goods
- Payments out of past savings
- Items should be Included: The following should be included in the national Income:
-
- Imputed value of services provided by owners of production units.
5. Expenditure Method
5.1 Concept of Expenditure Method
- This method measures national income as total spending on final goods and services produced within the nation during a year.
- National Income = Sum of all expenditures made for final goods and services at current market prices by households, firms and government during a year.
5.2 Categories of Expenditures
The total aggregate final expenditure on final output thus is the sum of four broad categories of expenditures:
| 1 | Consumption expenditure (C) |
|
| 2 | Investment expenditure (I) |
|
| 3 | Government expenditure (G) |
|
| 4 | Net exports (X – M) |
|
National income (from the expenditure side): Sum of above four categories of expenditure.
5.3 Steps of Expenditure Method
| (1) Identification economic units incurring final expenditure | All the economic units incurring final expenditure are classified under four groups:
|
| (2) Classification of final expenditure [GDPMP] | The final expenditure of above-mentioned units are estimated and classified under the following heads:
|
| (3) Calculation of Domestic Income i.e. NDPFC | NDPFC = GDPMP – Depreciation – Net Indirect Taxes |
| (4) Estimation of National Income (NNPFC) | NNPFC =NDPFC+ Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) |
5.4 Precautions for Expenditure Method
- Items Not Included: The following are NOT included in the national Income:
-
- Expenditure on intermediate goods
- Expenditure on Transfer Payments by government such as unemployment benefit, old age, etc.
- Purchase of second-hand goods
- Purchase of financial assets
- Items should be Included: The expenditure on own-account production will be included since these are productive services. For example: production for self-consumption, imputed value of owner-occupied houses, etc.
6. Measurement of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Market Prices
- GDP at Market Price: GDP is the total value of goods and services produced within the country during a year. This is calculated at market prices and is known as GDP at market prices.
- As per Dernberg: GDP at market price is the market value of the output of final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country during an accounting year.
- Methods: There are three different ways to measure GDP namely Product Method, Income Method and Expenditure Method.
| Product Method or value-added method |
|
| Income Method |
|
| Expenditure Method | This method focuses on goods and services produced within the country during one year. GDP by expenditure method includes:
(a) imports (M) |
Thus, GDP by expenditure method at market prices = C+ I + G + (X – M), where (X-M) is net export which can be positive or negative.
7. Measurement of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Factor Cost
GDP at Factor Cost = GDP at Market Price – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies.
8. Net Domestic Product (NDP)
Net Domestic Product = GDP at Factor Cost – Depreciation.
9. Nominal and Real GDP
| Nominal GDP | Real GDP |
| When GDP is measured on the basis of current price, it is called GDP at current prices or nominal GDP. | When GDP is calculated on the basis of fixed prices in some year, it is called GDP at constant prices or real GDP. |
Real GDP = GDP for the Current Year x Base Year (100) / Current Year Index
10. GDP Deflator
- GDP deflator is an index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP.
- It is a price index which is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP for the same year and multiplying it by 100.
- Thus, GDP Deflator =
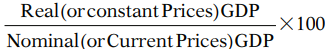
11. Measurement of Gross National Product (GNP) At Market Prices
- GNP is the total measure of the flow of goods and services at market value resulting from current production during a year in a country, including net income from abroad.
- GNP includes four types of final goods and services:
-
- Consumers’ goods and services to satisfy the immediate wants of the people;
- Gross private domestic investment in capital goods consisting of fixed capital formation, residential construction and inventories of finished and unfinished goods;
- Goods and services produced by the government; and
- Net exports of goods and services, i.e., the difference between the value of exports and imports of goods and services, known as net income from abroad.
- Important Factors: In this concept of GNP, there are certain factors that have to be taken into consideration:
-
- GNP is the measure of money.
- To avoid double-counting, the market price of only the final products and not the intermediary goods should be taken into account.
- If any goods and services have been rendered free of charge, then these are not included in the GNP.
- Only current year’s transactions are considered. It means, the transactions which do not arise from the produce of current year or which do not contribute in any way to production are not included in the GNP. The sale and purchase of old goods, and of shares, bonds and assets of existing companies are not included in GNP.
- The recipients do not provide any service in lieu of the payments received under social security, e.g., unemployment insurance allowance, old age pension, and interest on public loans. These are also not included in GNP.
- The profits earned or losses incurred on account of changes in capital assets as a result of fluctuations in market prices are not included in the GNP.
- The income earned through illegal activities is not included in the GNP. In fact, it is not known whether these things were produced during the current year or the preceding years. Moreover, many of these goods are foreign made and smuggled and hence not included in the GNP.
- Three Approaches to GNP: The estimated GNP would be the same under all the methods:
| Income Method | GNP = Wages and Salaries + Rents + Interest Dividends + Undistributed Corporate Profits + Mixed Income + Direct Taxes + Indirect Taxes + Depreciation + Net Income from abroad. |
| Expenditure Method | GNP=Private Consumption Expenditure (C) + Gross Domestic Private Investment (I) + Net Foreign Investment (X-M) + Government Expenditure on Goods and Services (G) = C+ I + (X-M) + G. |
| Value Added Method | GNP = Gross value added + net income from abroad. |
- GNP at Market Prices = GDP at Market Prices + Net Income from Abroad.
12. Measurement of Gross National Product (GNP) at Factor Cost
- GNP at factor cost is the sum of the money value of the income produced by and accruing to the various factors of production in one year in a country. It includes all items mentioned above under income method to GNP less indirect taxes.
- GNP at Factor Cost = GNP at Market Prices – Indirect Taxes + Subsidies.
13. Computation of Net National Product (NNP)
- NNP includes the value of the total output of consumption goods and investment goods. But the depreciation or capital consumption allowance is deducted from GNP.
- The word ‘net’ refers to the exclusion of that part of total output which represents depreciation.
- NNP at Market Prices= GNP at Market Prices – Depreciation.
- NNP at Factor Cost (National Income) = NNP at Market Prices – Indirect taxes+ Subsidies or NNPFC= GNP at Market Prices – Depreciation – Indirect taxes + Subsidies.
- Usually, NNPMP>NNPFC because indirect taxes exceed government subsidies. However, when government subsidies exceed indirect taxes, NNPMP<NNPFC.
14. Domestic Income
- Income generated (or earned) by factors of production within the country from its own resources is called domestic income or domestic product.
- It does not include income earned from abroad.
- Domestic Income = National Income-Net income earned from abroad.
|
The net national income earned from abroad may be positive or negative. |
|
|
|
15. Types of Income – Private, Personal, Disposable, Real and Per-Capita income
| Private Income
|
|
| Personal Income
|
|
| Private vs. Personal Income |
|
| Disposable Income
|
|
| Real Income |
|
| Per Capita Income
|
Per Capita Income for 2022 =
Real Per Capita Income for 2022 =
|
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied



 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
