Input Tax Credit (ITC) Eligibility Conditions – Key Requirements & Guidelines
- Blog|GST & Customs|
- 12 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 21 October, 2024

Input Tax Credit (ITC) eligibility conditions require that the registered recipient must possess valid tax invoices, debit notes, or other prescribed documents. The goods or services must have been received, and the supplier must have paid the relevant tax to the government. Additionally, the recipient should have filed the necessary GST returns, and the claimed ITC must be reflected in their GSTR-2B. ITC cannot be claimed on goods or services used for personal purposes, capital assets where depreciation is claimed on the tax amount, or in cases involving fraud or misrepresentation.
Table of the Contents
- Definitions of ITC (Input Tax Credit) & few terms used
- Eligibility and Conditions for Taking Input Tax Credit (ITC) (Section 16 Read with Rules 36 & 37 of CGST Rules)
- Apportionment, Determination & Reversal of ITC and Blocked Credit (Section 17 Read with Rules 38, 42 & 43 of CGST Rules)
Check out Taxmann's GST Mini Ready Reckoner which provides a 'basic working knowledge' of the GST mechanism, right from understanding the GST process, to the procedure and payment of tax & penalties under the law. This book will be helpful for beginners, students & professionals who wish to understand the concepts of GST Law in a simplified manner.
1. Definitions of ITC (Input Tax Credit) & few terms
Input Tax Credit: Input Tax Credit means the tax paid by the Registered Recipient of goods or services in the form of Central Tax (CGST), State Tax (SGST) or Union Territory Tax (UTGST) & Integrated Tax (IGST). Such tax is charged by the Registered Supplier at the time of sale of goods or services made to any Registered Recipient. It means this concept is applicable only for the buyer of goods or the recipient of services who has taken the GST registration.
ITC also includes:
- the GST paid on reverse charge basis by the registered recipient of supply on certain specified goods or services such as GTA, Advocate services etc.
- IGST paid on import of goods
For Example:
Janta Enterprises is a manufacturer and registered in the GST as regular taxpayer. GST payable on the sale of its final product is ` 450 and GST paid on the purchase made by Janta Enterprises is ` 300 Now ` 300 is called the ITC of Janta Enterprises, they can claim the ITC of ` 300 and they will need to deposit only ` 150 (450-300) as GST payable to the Government.
Registered Supplier: A person who has taken a GST registration and supplying the goods or services or both.
Registered Recipient: A person who has taken a GST registration and purchasing the goods or availing the services or both.
2. Eligibility and Conditions for Taking Input Tax Credit (ITC) (Section 16 Read with Rules 36 & 37 of CGST Rules)
The ITC can be claimed by any Registered Recipient only after fulfilling all the following conditions [i.e. from point (a) to (g)] –
(a) The Registered Recipient must be in possession of the requisite documents as follows: –
-
-
- Tax invoice or debit note issued by the registered supplier,
- Reverse charge invoice (In case of supplies on which recipient is liable to pay tax under reverse charge), which is generated & documented by the recipient himself,
- Bill of entry (In case of import of goods), proving the payment of GST on import,
- An Input Service Distributor Invoice or ISD credit note or any document issued by an ISD.
-
Please Note that the any of the above-mentioned documents must contain at least all the following five particulars for availing the ITC:
-
-
- The amount of tax charged,
- Description of goods or services,
- Total value of supply,
- GST No. of the supplier and recipient,
- Place of supply in case of transaction happened between two different States.
-
(aa) This condition is effective from 1st January 2022: The details of the purchase invoice or debit notes has been furnished by the supplier is his GSTR-1/IFF within the due time limit and such details are being reflected in the GSTR-2B of the registered person.
(b) The registered recipient has received the goods or services or both. Please note here that without actual or deemed receipt of goods/services, recipient cannot claim the ITC in his returns.
-
-
- For the purpose of this clause, it shall be deemed that the goods have been received by the registered recipient where the supplier has delivered the goods to any other person on the instructions of that registered recipient, before or during the movement of goods. (Bill to ship to model)
-
For Example:
“A” (Haryana) orders “B” (Rajasthan) to send the goods directly to C (Delhi). Here, the goods shall be deemed to be received by A (Haryana) as soon as the goods have been delivered by B (Rajasthan) to C (Delhi).
-
-
- It shall be deemed that the registered recipient has received the services where the services have been provided by the supplier to any person on the direction of and on account of such registered recipient.
- Where the goods against an invoice are received in lots or instalments, ITC can be claimed only after receiving the last lot.
-
For example: “A” (Haryana) purchased the goods from “B” (Rajasthan). “B” (Rajasthan) issued an invoice of ` 50,00,000 including GST dated 27-9-2019. Due to the high quantum of goods, “B” (Rajasthan) sent the goods to “A” (Haryana) in lots.
The 1st lot of the goods purchased was received by “A” (Haryana) on 29-9-2019
The 2nd lot of the goods purchased was received by “A” (Haryana) on 30-9-2019
The 3rd and last lot of the goods purchased against the invoice was received by “A” (Haryana) on 2-10-2019.
Hence, in the above example, “A” (Haryana) can claim the ITC on the invoice dated 27-9-2019 in the GST return for the month of Oct 2019, since the last lot was received on 2-10-2019.
(ba) This condition is effective from 1st October 2022: The details of input tax credit in respect of the said supply showing in the GSTR-2B of such registered person, has not been restricted.
(c) The registered supplier has paid the GST charged from the registered recipient to the government either in cash or through utilisation of eligible ITC.
The Amendment effective from 1st October, 2022
In case, the credit of input tax availed by a registered person against which the tax payable has not been paid by the supplier, then the ITC shall be reversed by the registered person along with applicable interest.
However, where the said supplier makes payment of the tax payable in respect of the aforesaid supplies, the said registered person may re-avail the amount of credit reversed by him.
(d) The registered supplier has filed its outward supply return (e.g. GSTR-1 in case of regular taxpayer) and the input invoices & debit notes are properly reflecting in the GSTR-2A of the registered recipient.
(e) The registered recipient has filed the requisite GST returns (Kindly refer GST returns chapter for the different types of returns)
(f) No ITC would be allowed on the capital assets if the depreciation is claimed on the tax part also.
For example: An asset is purchased for ` 1,18,000 (Basic value is ` 1,00,000 & GST charged @ 18% i.e. ` 18,000)
In this case: –
If the depreciation is claimed under income tax on ` 1,18,000, no ITC would be allowed.
If depreciation is claimed on ` 1,00,000, ITC of ` 18,000 would be allowed.
(g) A person who has taken GST registration under composition scheme, cannot claim input tax credit.
(h) ITC can be claimed by the registered recipient in respect of only those goods or services which are used or intended to be used in relation to his business.
(i) No ITC can be claimed in respect of any tax that has been paid for the reason of demand on account of fraud, deliberate misstatement or concealment of facts or ceasing of goods.
2.1 New restriction imposed on the availment of ITC with effect from 9-10-2019 (Rule 36(4) in CGST Rules, 2017)
This new rule was inserted by the government through CGST (Sixth Amendment) Rules, 2019 and it is effective from 9th of October, 2019.
Eligibility before 9-10-2019: Before this rule, the registered recipients used to avail the whole eligible input on the basis of their input invoices against goods or services received during the tax period.
Eligibility from 9-10-2019 to 31-12-2019: Now with effect from 9-10-2019, the registered recipient can only avail the eligible input which is 20% of the eligible input reflecting in its GSTR-2A for that tax period in addition to the eligible input reflecting in the GSTR-2A.
(Eligible ITC existing in 2A + 20% of the eligible ITC existing in 2A) = Provisional ITC maximum allowable in a tax period
Eligibility from 1-1-2020 to 31-12-2020: Now with effect from 1-1-2020, the registered recipient can only avail the eligible input which is 10% of the eligible input reflecting in its GSTR-2A for that tax period in addition to the eligible input reflecting in the GSTR-2A.
(Eligible ITC existing in 2A + 10% of the eligible ITC existing in 2A) = Provisional ITC maximum allowable in a tax period
Eligibility from 1-1-2021 to 31-12-2021: Now with effect from 01-01-2021, the registered recipient can only avail the eligible input which is 5% of the eligible input reflecting in its GSTR-2A for the tax period in addition to the eligible input reflecting in the GSTR-2A.
(Eligible ITC existing in 2A + 5% of the eligible ITC existing in 2A) = Provisional ITC maximum allowable in a tax period.
Eligible Input: Eligible input means the input which is fulfilling all the eligibility conditions as prescribed above excluding the blocked credit under section 17(5) and the reversals required under rules 42, 43 & 37 if any.
Please note that the said condition shall apply cumulatively for the period February, March, April, May, June, July and August, 2020 and the return in FORM GSTR-3B for the tax period September, 2020 shall be furnished with the cumulative adjustment of input tax credit for the said months in accordance with the condition above.
It means that the 10% restriction on ITC can be worked upon cumulatively for the months (Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug 2020) in the GSTR-3B of Sep 2020 month.
Some conditions of this new rule:
|
For Example: –
*Please note that the actual ITC which can be claimed cannot exceed the eligible ITC as per books. Now if the balance input is reflected in GSTR-2A of further tax periods, the calculation of the eligible ITC for those inputs would be as follows: – |
||||||||||||||||||||
*Please note that the actual ITC which can be claimed, cannot exceed the balance eligible ITC as per books. |
Eligibility from 01-01-2022: Now with effect from 01-01-2022, the registered recipient can only avail the eligible input which is reflecting in its GSTR-2B for the tax period.
(Eligible ITC existing in 2B = ITC maximum allowable in a tax period)
2.2 Time limit or deadlines for availing ITC
A registered person cannot take the input tax credit after the following date:
- Due date of filing of GST Return (return in which ITC is availed i.e. GSTR-3B for regular taxpayers) for the month of September following the end of financial year to which the ITC relates.
- Actual Date of furnishing of GST annual return (i.e. GSTR-9)
Whichever is earlier………
For Example: – An input of ` 10,000 belongs to Jan 2019, which was not taken in the GST
return of that particular month. Now the last date up to which, this input can be taken is as follows:
- Due date of filing of GST return of September following the end of financial year to which the ITC relates means: – Input relates to year 2018-19, hence last date to file September 2019-20 GST return is: – 20th Oct 2019 (GSTR-3B)
- Actual date of furnishing of annual return: – the actual date on which annual return of F.Y. 2018-19 is filed, let us assume on 11th Nov 2019.
Hence, in this case the last date of taking GST input of FY 2018-19 would be 20th Oct 2019. (Earlier of 20th Oct 2019 & 11th Nov 2019)
The most important amendment in the deadlines to avail the ITC (Effective from 1st October, 2022) A registered person cannot take the input tax credit after the following date: - - 30th November following the end of financial year to which the ITC relates. or - Actual Date of furnishing of GST annual return (i.e. GSTR-9) Whichever is earlier………
NOTE NO. 1
For finding that ITC is related to which FY, the following elements shall be considered:
- For ITC on invoice: Date of that invoice
- For ITC on Debit Note: Date of the invoice for which such debit note is issued

| Amendments effective from 1st January, 2021
The date of the debit note will be considered for availing input tax credit. With this amendment, ITC in respect of a debit note issued in, say, FY 2019-20 for an invoice of FY 2018-19 can now be claimed by the recipient by the due date of September 2020 return or the date of filing annual return of FY 2019-20, whichever is earlier. |
| Relaxation notified by the Government during pandemic of COVID-19, for the deadlines already prescribed earlier in the Act & rules in relation to the GST compliances
In case, – the deadline in the above case (4.2.2) falls during the period from 20th March 2020 to 30th August 2020 and, – where compliance of such action has not been made within such time, Then the time limit for the compliance of such action shall be extended up to 31st August 2020. Relaxation for the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic In case, – the deadline in the above case falls during the period from 15th April 2021 to 30th May 2021 and, – where compliance of such action has not been made within such time. Then the time limit for the compliance of such action shall be extended up to 31st May 2021. |
2.3 Restriction on the availment of ITC if the payment of invoice is not made within 180 days by the registered recipient (Rule 37 of CGST Rules)
A registered person,
- who has claimed the ITC on any inward supply, other than the supplies on which tax is payable on reverse charge basis,
- but fails to pay to the supplier, the amount towards the value of such supply [whether wholly or partly w.e.f. 01st October, 2022] along with the tax payable thereon,
- within 180 days from the date of invoice,
shall pay [or reverse w.e.f. 01st October, 2022] an amount equal to the input tax credit availed in respect of such supply [proportionate to the Invoice amount not paid to the supplier w.e.f. 01st October, 2022] along with interest payable thereon under section 50.
Such reversal shall be done in GSTR-3B for the tax period immediately following the period of 180 days from the date of the issue of the invoice.
*Here reverse charge inward supplies are not included in goods or services. It means that the condition of 180 days is not applicable in case of inward supplies on which RCM is applicable.
For Example: –
A Ltd. purchased goods from B Ltd. of ` 1,18,000 (Basic ` 1,00,000 & ` 18,000 tax thereon) against invoice dated 1st June 2018. Here, if A Ltd. does not pay the invoice amount to B Ltd. within 180 days of the date of invoice (i.e. till 27th Nov 2018), the Input of ` 18,000 will have to be added to the Output tax liability of A Ltd. along with interest @ 18% p.a. in the GST return of Nov 2018 month.

| Relaxation notified by the Government during pandemic of COVID-19, for the deadlines already prescribed earlier in the Act & rules in relation to the GST compliances
In case, – the deadline in the above case (4.2.3) falls during the period from 20th March 2020 to 30th August 2020 and, – where compliance of such action has not been made within such time, Then the time limit for the compliance of such action shall be extended up to 31st August 2020. Relaxation for the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic In case, – the deadline in the above case falls during the period from 15th April 2021 to 30th May 2021 and, – where compliance of such action has not been made within such time. Then the time limit for the compliance of such action shall be extended up to 31st May 2021. |
3. Apportionment, Determination & Reversal of ITC and Blocked Credit (Section 17 Read with Rules 38, 42 & 43 of CGST Rules)
3.1 Determination & Reversal of Input Tax Credit in respect of inputs & input services (Rule 42 of CGST Rules)
Here in this topic, we are going to explain the followings: –
- Reversal of ITC in case the goods or services are being used for business & personal purposes.
- Reversal of ITC in case the goods or services are being used for providing the taxable and exempt supplies.
- The final calculation for the reversal of common ITC at the end of the year in both of the cases mentioned above.
- The final calculation for the reversal of common ITC in case of construction services provided to the pre-fixed buyer for a project.
- The final calculation for the reversal of common ITC in case of construction services provided to the pre-fixed buyer for a project containing commercial portion also.
- The option provided to the banking company or a financial institution including NBFCs for the availment and reversal of ITC.
Common ITC: It means the ITC on such goods or services which are commonly used for business & personal purpose and commonly used for providing the taxable & exempt supplies.
3.1.1 Where the goods or services on which GST is charged, are used for the following purposes: (1st Case)
- Business purpose
- Personal purpose
In this case the ITC would be allowed & reversed as per the following rules: –
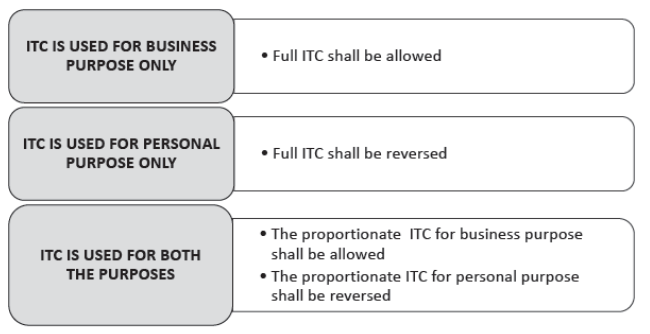
For Example: – A Ltd. is a trader, the total ITC on goods or services purchased is ` 1,00,000. Now there are three conditions on availing the ITC on such goods & services: –
- Fully used for business purpose: ITC of ` 1,00,000 is allowed
- Fully used for personal purpose: ITC of ` 1,00,000 is to be reversed
- 60% used for business purpose & 40% used for personal purpose: – ITC of ` 60,000
Answer: (1,00,000 × 60%) is allowed and ITC of ` 40,000 (1,00,000 × 40%) is to be reversed.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied






 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA

electric cable purchased for plant & machinery is eligible for itc or not?
“Under GST law, a registered person is entitled to take ITC of tax charged on any supply of goods/services or both which are used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of his business. Further, Section 17(5) of the CGST Act, 2017 provides list of few goods and services on which ITC is not available.
Subject to satisfaction of other conditions relating to Input Tax Credit, the Electric cables purchased for plant and machinery would be eligible for the Input Tax Credit.”
super message Sir thank you so much your detailed summary
We have filed GSTR-3B for the Period March 2018 on 24-04-2019, actual due date for claiming input relating to 2017-18 is 23-04-2019. but we filed on 24-04-2019 i.e one day delay.
Now Department Restricted that ITC and charged interest and penalty.
Please confirm how to solve the issue and how much interest & penalty applicable
can ITC claim on interest on overdue payment
We understand that the given value of interest pertains to the addition in the value of supply of goods or services originally supplied as provided by Section 15(2)(d) of the CGST Act. There is no restriction as such on claiming the input tax credit of such addition. Hence, upon fulfilment of the general conditions, ITC can be claimed.
I have purchased dumper for transporting materials . Should I get the input tax credit for the purchasing the new dumper?
Post February 01, 2019, vide CGST Amendment Act, 2018, ITC in respect of all goods transportation vehicles is allowed. Prior to this amendment, the law used to provide a few restrictions relating to the claim of ITC in respect of Goods transport vehicles.