[FAQs] on Strategic Management Process
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 9 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 16 June, 2023
Check out Taxmann's Enterprise Information Systems & Strategic Management (EIS SM) | CRACKER which covers all past exam questions & detailed answers for the CA-Inter exam by ICAI till May 2023, RTPs & MTPs of ICAI. It also features chapter-wise marks distribution, previous exam trend analysis & ICAI study material comparison. CA Inter | Nov. 2023 Exam
FAQ 1. What is the difference between Strategic Plan and Operational Plan?
- Strategic plans are made by the senior management for the entire organization after taking into account the organization’s strength and weaknesses in the light of opportunities and threats in the external environment. They involve acquisition and allocation of resources for the attainment of organizational objectives.
- But operational plans on the other hand are made at the middle and lower level management. They specify details on how the resources are to be utilized efficiently for the attainment of objectives.
FAQ 2. What is Strategic Planning?
- It is the process of:
-
- determining the objectives of the firm,
- resources required to attain these objectives and
- formulation of policies to govern the acquisition,
- use and disposition of resources.
- Strategic planning involves a fact of interactive and overlapping decisions leading to the development of an effective strategy for the firm.
- Strategic planning determines where an organization is going over the next year or more and the ways for going there.
- The process is organization-wide, or focused on a major function such as a division or other major function.
FAQ 3. How can a company deal with strategic uncertainty?
- Strategic uncertainty denotes the uncertainty that has crucial implications for the organization.
- A typical external analysis will emerge with dozens of strategic uncertainties.
- To be manageable, they need to be grouped into logical clusters or themes.
- It is then useful to assess the importance of each cluster in order to set priorities with respect to Information gathering and analysis.
FAQ 4. What is Strategic Decision Making? What tasks are performed by a strategic manager?
- Decision making
-
- is a managerial process of
- selecting the best course of action out of several alternative courses
- for the purpose of accomplishment of the organizational goals.
- Decisions may be operational, i.e.,which relate to general day-to-day operations.
- They may also be strategic in nature.
- According to Jauch and Glueck
“Strategic decisions encompass the
- definition of the business,
- functions to be performed
- major policies needed for the organization,
- products to be handled,
- markets to be served,
to execute these decisions to achieve the strategic objectives.”
The primary task of the strategic manager is conceptualizing, designing and executing company strategies. For this purpose, his tasks include:
- Defining the mission and goals of the organization.
- Determining what businesses it should be in.
- Allocating resources among the different businesses.
- Formulating and implementing strategies that span individual businesses.
- Providing leadership for the organization.
FAQ 5. What are the major dimensions of strategic decisions?
The major dimensions of strategic decisions are as follows:
- Strategic decisions are likely to have a significant impact on the long-term prosperity of the firm: Generally, the results of strategic implementation are seen on a long-term basis and not immediately.
- Strategic decisions are future oriented: Strategic thinking involves predicting the future environmental conditions and how to orient for the changed conditions.
- Strategic decisions require top-management involvement: Strategic decisions involve thinking in totality of the organization. Hence, problems calling for strategic decisions require to be considered by the top management.
- Strategic decisions involve commitment of organizational resources: For example, Strategic decision to launch a new project by a firm requires allocation of huge funds and assignment of a large number of employees.
- Strategic decisions usually have major multifunctional or multi-business consequences: As they involve organization in totality they affect different sections of the organization with varying degree.
- Strategic decisions necessitate consideration of factors in the firm’s external environment: Strategic focus in organization involves orienting its internal environment to the changes of external environment.
FAQ 6. What is strategic intent? What are the elements of strategic intent?
- Strategic Management is defined as a dynamic process of formulation, implementation, evaluation, and control of strategies to realize the organization’s strategic intent.
- Strategic intent refers to purposes of what the organization strives for.
- Senior managers must define “what they want to do” and “why they want to do”.
- “Why they want to do” represents strategic intent of the firm.
- Clarity in strategic intent is extremely important for the future success and growth of the enterprise, irrespective of its nature and size.
- Strategic intent can be understood as the philosophical base of strategic management.It implies the purposes, which an organization endeavors to achieving.
- It is a statement that provides a perspective of the means, which will lead the organization, reach its vision in the long run.
- Strategic intent gives an idea of what the organization desires to attain in future.
- It answers the question what the organization strives or stands for? It indicates the long-term market position, that the organization desires to create or occupy and the opportunity for exploring new possibilities.
- Strategic intent provides the framework within which the firm would adopt a predetermined direction and would operate to achieve strategic objectives.
- Strategic intent could be in the form of vision and mission statements for the organization at the corporate level.
- It could be expressed as the business definition and business model at the business level of the organization.
- Strategic intent is generally stated in broad terms but when stated in precise terms it is an expression of aims to be achieved operationally, i.e., goals and objectives.
Elements of Strategic Intent are:
- Vision: Vision implies the blueprint of the company’s future position. It describes where the organization wants to land. It depicts the organization’s aspirations and provides a glimpse of what the organization would like to become in future. Every sub system of the organization is required to follow its vision.
- Mission: Mission delineates the firm’s business, its goals and ways to reach the goals. It explains the reason for the existence of the firm in the society. It is designed to help potential shareholders and investors understand the purpose of the company. A mission statement helps to identify, ‘what business the company undertakes.’ It defines the present capabilities, activities, customer focus and role in society.
- Business Definition: It seeks to explain the business undertaken by the firm, with respect to the customer needs, target markets, and alternative technologies. With the help of business definition, one can ascertain the strategic business choices. Organizational restructuring also depends upon the business definition.
- Business Model: The business model, as the name implies is a strategy for the effective operation of the business, ascertaining sources of income, desired customer base, and financial details. Rival firms, operating in the same industry rely on the different business model due to their strategic choice.
- Goals and Objectives:
-
- These are the base of measurement.
- Goals are the end results, that the organization attempts to achieve.
- On the other hand, objectives are time-based measurable targets, which help in the accomplishment of goals. These are the end results which are to be attained with the help of an overall plan, over the particular period.
- However, in practice, no distinction is made between goals and objectives and both the terms are used interchangeably.
The vision, mission, business definition, and business model explain the philosophy of the organization but the goals and objectives represent the results to be achieved in multiple areas of business.
FAQ 7. What is Strategic Vision?
- Strategic vision
-
- delineates Organisation’s aspirations for the business,
- providing a panoramic view of the position where the Organisation is going. (panoramic means: with a view of wide area)
- Strategic vision points out an Organisation in a particular direction, charts a strategic path for it to follow in preparing for the future, and moulds organizational identity.
- A Strategic vision is a road map of a company’s future – providing specifics about:
-
- technology
- the capabilities it plans to develop,
- the geographic and product markets to be pursued,
- customer focus,
- and the kind of company that management is trying to create.
FAQ 8. What are the Essentials of a strategic vision?
- The entrepreneurial challenge in developing a strategic vision is to think creatively about how to prepare a company for the future.
- Forming a strategic vision is an exercise in intelligent entrepreneurship.
- A well-articulated strategic vision creates enthusiasm among the members of the organisation.
- The best-worded vision statement clearly illuminates the direction in which organization is headed.
FAQ 9. Why an organisation should have a mission? What considerations are to be kept in mind while writing a good mission statement of a company?
- Mission statement is an answer to the question “Who we are and what we do” and hence has to focus on the organisation’s present capabilities, focus activities and business makeup.
- An organisation’s mission states what customers it serves, what need it satisfies, and what type of product it offers.
- Mission is an expression of the growth ambition of the organisation.
- A company’s mission statement is typically focused on its present business scope-“who we are and what we do”; mission statements broadly describe an organizations present capabilities, customer focus activities and business makeup.
- Organization should have a mission on account of the following reasons:
-
- To ensure unanimity of purpose within the organization.
- To develop a basis, or standard, for allocating organizational resources.
- To provide a basis for motivating the use of the organization’s resources.
- To establish a general tone or organizational climate.
- To serve as a focal point for those who can identify with the organization’s purpose and direction.
- To facilitate the translation of objective and goals into a work structure involving the assignment of tasks to responsible elements within the organization.
- To specify organizational purposes and the translation of these purposes into goals in such a way that cost, time, and performance parameters can be assessed and controlled.
- The following points must be considered while writing a mission statement of a company.
(i) To establish the special identity of the business – one that typically distinct it from other similarly positioned companies.
(ii) Needs which business tries to satisfy, customer groups it wishes to target and the technologies and competencies it uses and the activities it performs.
(iii) Good mission statements should be unique to the organisation for which they are developed.
(iv) The mission of a company should not be to make profit. Surpluses may be required for survival and growth, but cannot be mission of a company.
Mission statement should reflect the philosophy of the organizations that is perceived by the senior managers. A good mission statement should be precise, clear, feasible, distinctive and motivating.
FAQ 10. What are the Goals and Objectives of an organization?
- Business organization translates their vision and mission into goals and objectives.
- As such the term objectives are synonymous with goals, however, some authors make an attempt to distinguish the two.
- Goals are open-ended attributes that denote the future states or outcomes.
- Objectives are close-ended attributes which are precise and expressed in specific terms. Thus, the Objectives are more specific and translate the goals to both long term and short term perspective.
- All organizations have objectives. The pursuit of objectives is an unending process such that organizations sustain themselves. They provide meaning and sense of direction to organizational endeavour.
- Organizational structure and activities are designed and resources are allocated around the objectives to facilitate their achievement. They also act as benchmarks for guiding organizational activity and for evaluating how the organization is performing.
FAQ 11. What are the characteristics which must be possess by objectives, to be meaningful to serve the intended role?
Objectives, to be meaningful to serve the intended role, must possess the following characteristics:
- They should be concrete and specific.
- They should be measurable and controllable.
- They should be facilitative towards achievement of mission and purpose.
- Different objectives should correlate with each other.
- They should be related to a time frame.
- They should be challenging.
- They should provide the basis for strategic decision-making.
- They should provide standards for performance appraisal.
- Objectives should define the organization’s relationship with its environment.
- Objectives should be set within the constraints of organisational resources and external environment.
FAQ 12. What is strategic management process?
Identifying an organization’s vision, mission, goals and objectives, is the starting point for strategic management process.
The strategic management process is dynamic and continuous.
A change in any one of the major components in the model can necessitate a change in any or all of the other components. For instance:
- a shift in the economy could represent a major opportunity and require a change in long-term objectives and strategies;
Therefore, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation activities should be performed on a continual basis, not just at the end of the year or semi-annually. The strategic management process never really ends.
The strategic management process can best be studied and applied using a model. Every model represents some kind of process. The model illustrated in the Figure: Strategic Management Model is a widely accepted, comprehensive.
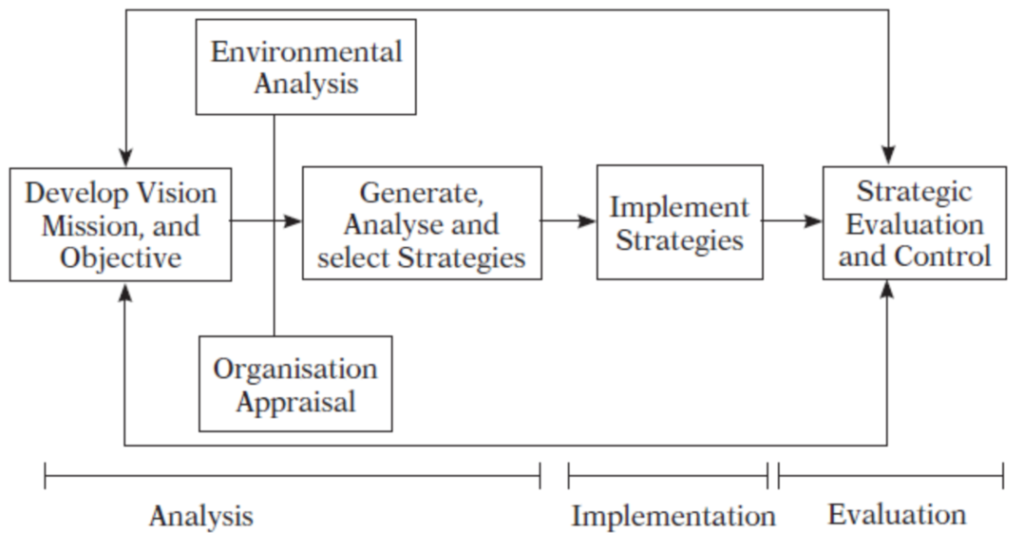
This model like any other model of management does not guarantee sure-shot success, but it does represent a clear and practical approach for formulating, implementing, and evaluating strategies. Relationships among major components of the strategic management process are shown in the model.
Generally, there is give-and-take among hierarchical levels of an organization. Many organizations conduct formal meetings semi-annually to discuss and update the firm’s vision/mission, opportunities/threats, strengths/weaknesses, strategies, objectives, policies, and performance. Creativity from participants is encouraged in meeting.
Good communication and feedback are needed throughout the strategic management process.
FAQ 13. What are the Stages in Strategic Management?
Strategic management involves the following stages:
- Developing a strategic vision and formulation of statement of mission, goals and objectives.
- Environmental and organizational analysis.
- Formulation of strategy.
- Implementation of strategy.
- Strategic evaluation and control
FAQ 14. What are the principal aspects of strategy-execution process, which are included in most situations?
In most situations, strategy-execution process includes the following principal aspects:
- Developing budgets that steer ample resources into those activities critical to strategic success.
- Staffing the organization with the needed skills and expertise, consciously building and strengthening strategy-supportive competencies and competitive capabilities, and organizing the work effort.
- Ensuring that policies and operating procedures facilitate rather than impede effective execution.
- Using the best-known practices to perform core business activities and pushing for continuous improvement.
- Installing information and operating systems that enable company personnel to better carry out their strategic roles day in and day out.
- Motivating people to pursue the target objectives energetically.
- Creating a company culture and work climate conducive to successful strategy implementation and execution.
- Exerting the internal leadership needed to drive implementation forward and keep improving strategy execution. When the organization encounters stumbling blocks or weaknesses, management has to see that they are addressed and rectified quickly.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied



 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA
