[Analysis] Estate Planning Through Family Offices – Benefits | Types | Tax Strategies
- Other Laws|Blog|
- 4 Min Read
- By Taxmann
- |
- Last Updated on 29 February, 2024

By CA. Darshak Shah – Partner | S N & Co.
Table of Contents
- Why Family Office is Beneficial?
- Types of Family Offices
- Why owner would not distribute wealth directly?
- Deciding Factors in Structuring
- Structuring of Family Office
- Tax Implications In Family Office
1. Why Family Office is Beneficial?
- For the Protection of wealth
- Single point professional Control of all your businesses and assets
- FO becomes vital where there are multiple decision makers in a family in different jurisdictions
-
- Allows for the synchronization of business considerations with personal succession goals
- Retaining sensitive information and select sharing on a need-to-know-basis
-
- Members choosing to reside and purchase assets in multiple jurisdictions, or the inheritance plans
- To ensure proper control and risk management
2. Types of Family Offices
- Single-Family Office (SFO): A SFO is a private organization that exclusively manages the wealth and affairs of a single family, highly customizable
- Multi-Family Office (MFO): Manages the affairs of multiple families, often formed when several family offices pool resources for the running of the office which gives benefit of Economies of Scale
- Virtual Family Office (VFO): Run online rather than at a brick-andmortar office, usually to keep the operation lean and efficient
3. Why owner would not distribute wealth directly?
- Perpetuity: The family office can help the family in defining a clear family purpose and therefore support them in creating a legacy across the different generations.
- Asset protection
- Tax optimization
To avoid disputes between family members in future
- Provides a framework for exit.
- Such framework provide cooling-off period at the time of separation of any member which may solve disputes with the time.
- Dispute boards comprising an independent committee established by the parties to help avoid and overcome disputes.
- Role of independent non-family members in leadership to address the potential that future generations lack the interest or ability to run FO affairs.
4. Deciding Factors in Structuring
- Objective of Creating FO (like investment purpose, for Succession planning, Tax optimization)
- Selection of Jurisdiction/s
- Consideration of Legal Entity
- Tax Implications
5. Structuring of Family Office
- FO in Singapore – Case where Individual is having the funds in his own accounts to dispose.
- Where owner incorporates the co. in Singapore then contributes such shares as assets as settlor in the Trust where family members are beneficiaries
Case When owner does not have funds in own hands to dispose it directly i.e. funds in company to dispose
- Route it through company
- Firstly need to incorporate Singapore company through Existing Indian Company,
- Then Demerge the Singapore shares asset in the new company
- The shares of the new entity will be with the owners, now they can contribute these shares to the trust as settlor for the beneficiares of the trust
6. Tax Implications In Family Office
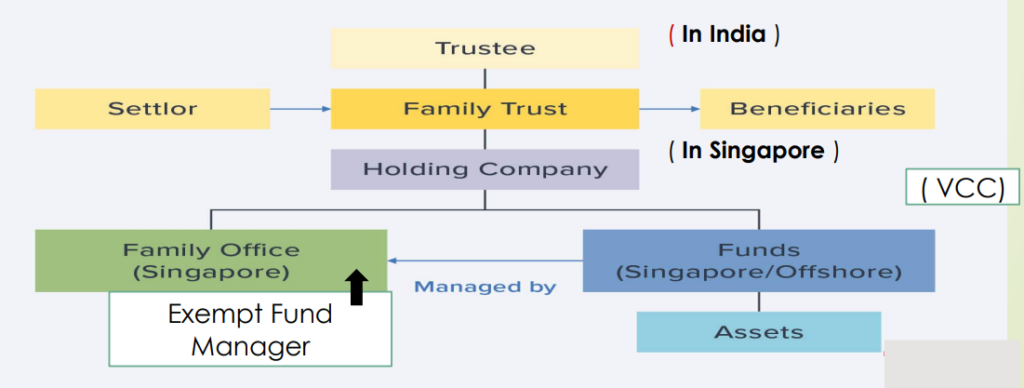
6.1 Trust Structure – Taxation through Trusts
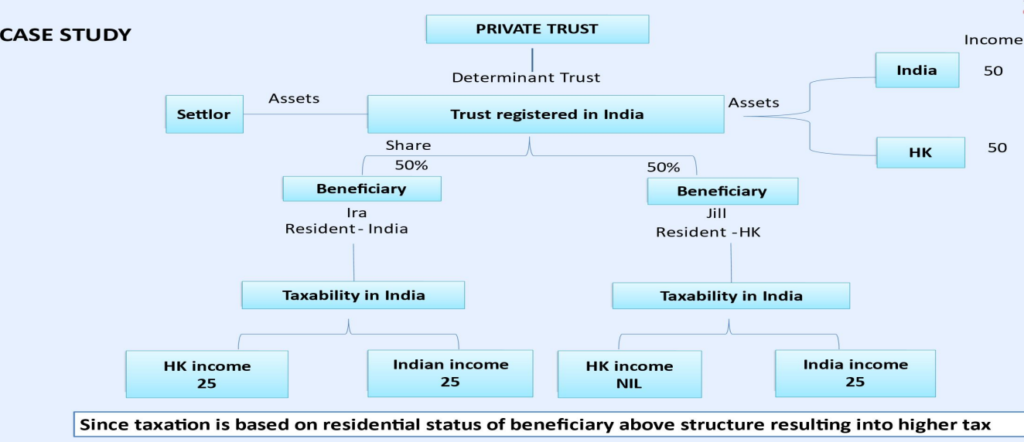
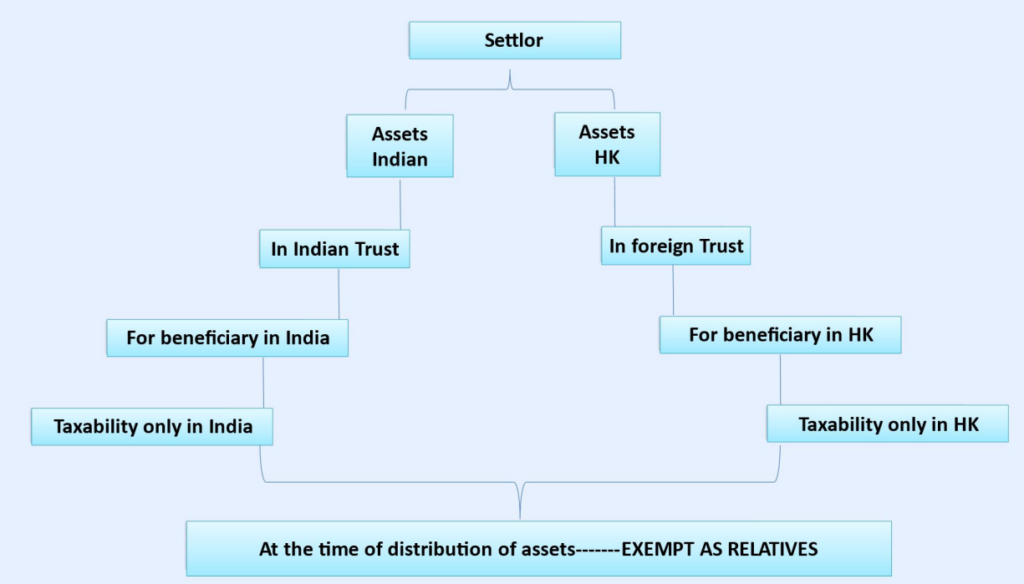
6.2 Taxability of Trust
| Determinate | Discretionary | Foreign | |
| Status of trust | Beneficiary to extent of share | Beneficiary to extent of share If different then status of trustee |
Beneficiary to extent of share |
| Residential Status | Beneficiary to extent of share | Beneficiary to extent of share If different then status of trustee | Beneficiary to extent of share |
| Taxability in hands of | Trustee or beneficiary | Income distributed – Beneficial/trustee Income not distributed – Trustee |
Refer – Table B |
| Rate of Tax | Normal rate of beneficiary [B&P @ MMR] Or AOP rate | MMR or AOP [exception cases] |
Table B
| Revocable | Indian settlor | Taxable in his hand |
| Revocable | Foreign settlor | Based on status of beneficiary |
| Irrevocable | POEM | World income is taxable |
| Irrevocable | Foreign & Indian beneficiaries | Indian beneficiary taxed on accrual |
6.3 Tax Benefits of setting up of FO
- Effective Tax Saving by selecting proper jurisdictions (IFSC, Singapore, UAE)
- Less limits applicable and compliances of FEMA by using proper structure eventually more returns
- Example – SFO/MFO in Singapore gets tax exemptions arised from invest by SFO.
6.4 Family Offices in Gift City and its Tax Benefits
- Investment in overseas real estate is allowed for FIF
- Succession Planning can be done effectively through trust structure. Private trust structure can serve to meet long term and specific family goals.
- 100% Tax exemption for 10 consecutive years and GST exemption.
- FIF can borrow funds and engage in leveraging activities.
- Relaxed FEMA rules from restrictions on overseas portfolio investment.
- Powerful tool for building a diversified portfolio, reaching beyond domestic assets. A qualifying Indian entity, which must be 90% familyowned, can contribute up to 50% of its net worth.
- FIFs have the access to banks ( International Bank also ) situated in GIFT City, where they can potentially take on leverage in the form of loans.
Disclaimer: The content/information published on the website is only for general information of the user and shall not be construed as legal advice. While the Taxmann has exercised reasonable efforts to ensure the veracity of information/content published, Taxmann shall be under no liability in any manner whatsoever for incorrect information, if any.

Taxmann Publications has a dedicated in-house Research & Editorial Team. This team consists of a team of Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Lawyers. This team works under the guidance and supervision of editor-in-chief Mr Rakesh Bhargava.
The Research and Editorial Team is responsible for developing reliable and accurate content for the readers. The team follows the six-sigma approach to achieve the benchmark of zero error in its publications and research platforms. The team ensures that the following publication guidelines are thoroughly followed while developing the content:
- The statutory material is obtained only from the authorized and reliable sources
- All the latest developments in the judicial and legislative fields are covered
- Prepare the analytical write-ups on current, controversial, and important issues to help the readers to understand the concept and its implications
- Every content published by Taxmann is complete, accurate and lucid
- All evidence-based statements are supported with proper reference to Section, Circular No., Notification No. or citations
- The golden rules of grammar, style and consistency are thoroughly followed
- Font and size that’s easy to read and remain consistent across all imprint and digital publications are applied



 CA | CS | CMA
CA | CS | CMA

One thought on “[Analysis] Estate Planning Through Family Offices – Benefits | Types | Tax Strategies”